Deploy RabbitMQ on Google Cloud C4A (Arm-based Axion VMs)
Introduction
Learn about RabbitMQ and Google Axion C4A
Create a firewall rule on GCP
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on GCP
Install RabbitMQ
Validate RabbitMQ installation
RabbitMQ use case 1: event processing with Python workers
RabbitMQ use case 2: WhatsApp notification
Next Steps
Deploy RabbitMQ on Google Cloud C4A (Arm-based Axion VMs)
Install RabbitMQ on GCP SUSE Arm64 VM
In this section you’ll install RabbitMQ on a Google Cloud Platform SUSE Linux Arm64 virtual machine using RPM packages for both Erlang and RabbitMQ Server.
RabbitMQ needs Erlang to be installed before setting up the server.
Prerequisites
- GCP SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (Arm64)
- Root or sudo privileges
- Outbound internet access
Refresh system repositories
Update the system’s package list to get the latest available software from repositories.
sudo zypper refresh
Install required system utilities
Install the basic tools needed to download and manage packages.
sudo zypper install -y curl wget gnupg tar socat logrotate
Download Erlang RPM (Arm64)
RabbitMQ depends on Erlang. Download the Erlang RPM compatible with the Arm64 architecture.
wget https://github.com/rabbitmq/erlang-rpm/releases/download/v26.2.5/erlang-26.2.5-1.el8.aarch64.rpm
sudo rpm -Uvh erlang-26.2.5-1.el8.aarch64.rpm
Verify Erlang installation
Confirm that Erlang is installed correctly:
erl -eval 'io:format("~s~n", [erlang:system_info(system_version)]), halt().' -noshell
The output is similar to:
Erlang/OTP 26 [erts-14.2.5] [source] [64-bit] [smp:4:4] [ds:4:4:10] [async-threads:1] [jit]
Download RabbitMQ server RPM
Download the RabbitMQ Server RPM package.
wget https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/releases/download/v4.2.0/rabbitmq-server-4.2.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm
sudo rpm -Uvh rabbitmq-server-4.2.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm
RabbitMQ version 3.11.0 introduced significant performance enhancements for Arm-based architectures. This version needs Erlang 25.0 or later, which brings Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation and modern flame graph profiling tooling to both x86 and Arm64 CPUs. These features result in improved performance on Arm64 architectures.
View the release notes for more information.
The Arm Ecosystem Dashboard recommends RabbitMQ version 3.11.0, the minimum recommended on Arm platforms.
Enable and start RabbitMQ service
Enable RabbitMQ to start automatically on boot and start the service immediately.
sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server --now
Verify RabbitMQ service status
Check the status of the RabbitMQ service.
sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server
The service should be in an active (running) state.
● rabbitmq-server.service - Open source RabbitMQ server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rabbitmq-server.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2026-01-09 14:50:52 UTC; 3s ago
Main PID: 3953 (beam.smp)
Tasks: 53
CPU: 2.432s
CGroup: /system.slice/rabbitmq-server.service
├─ 3953 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/beam.smp -W w -MBas ageffcbf -MHas ageffcbf -MBlmbcs 512 -MHlmbcs 512 -MMmcs 30 -pc unicode -P 1048576 -t 5000000 -stbt db -zdbbl >
├─ 3967 erl_child_setup 32768
├─ 4014 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/inet_gethost 4
├─ 4015 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/inet_gethost 4
├─ 4024 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/epmd -daemon
└─ 4077 /bin/sh -s rabbit_disk_monitor
Enable RabbitMQ management plugin
Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin to access the web-based dashboard.
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Restart RabbitMQ
Restart RabbitMQ to apply plugin changes.
sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
Verify RabbitMQ version
Confirm the installed RabbitMQ version:
sudo rabbitmqctl version
The output is similar to:
4.2.0
Access RabbitMQ management UI
Create a new RabbitMQ user for remote access.
Create a new admin user by running these commands on the VM:
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user admin StrongPassword123
sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / admin ".*" ".*" ".*"
Replace StrongPassword123 with a strong, unique password. For production environments, use environment variables or a secrets management system instead of hardcoding passwords.
Log in to Management UI
Now, test it from outside the VM. Open a web browser on your local machine (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) and enter the following URL and credentials in the address bar:
- URL: http://<VM_IP>:15672
- Username: admin
- Password: StrongPassword123
Replace <VM_IP> with the public IP of your GCP VM.
If everything is configured correctly, you see a RabbitMQ login page in your browser that looks like this:
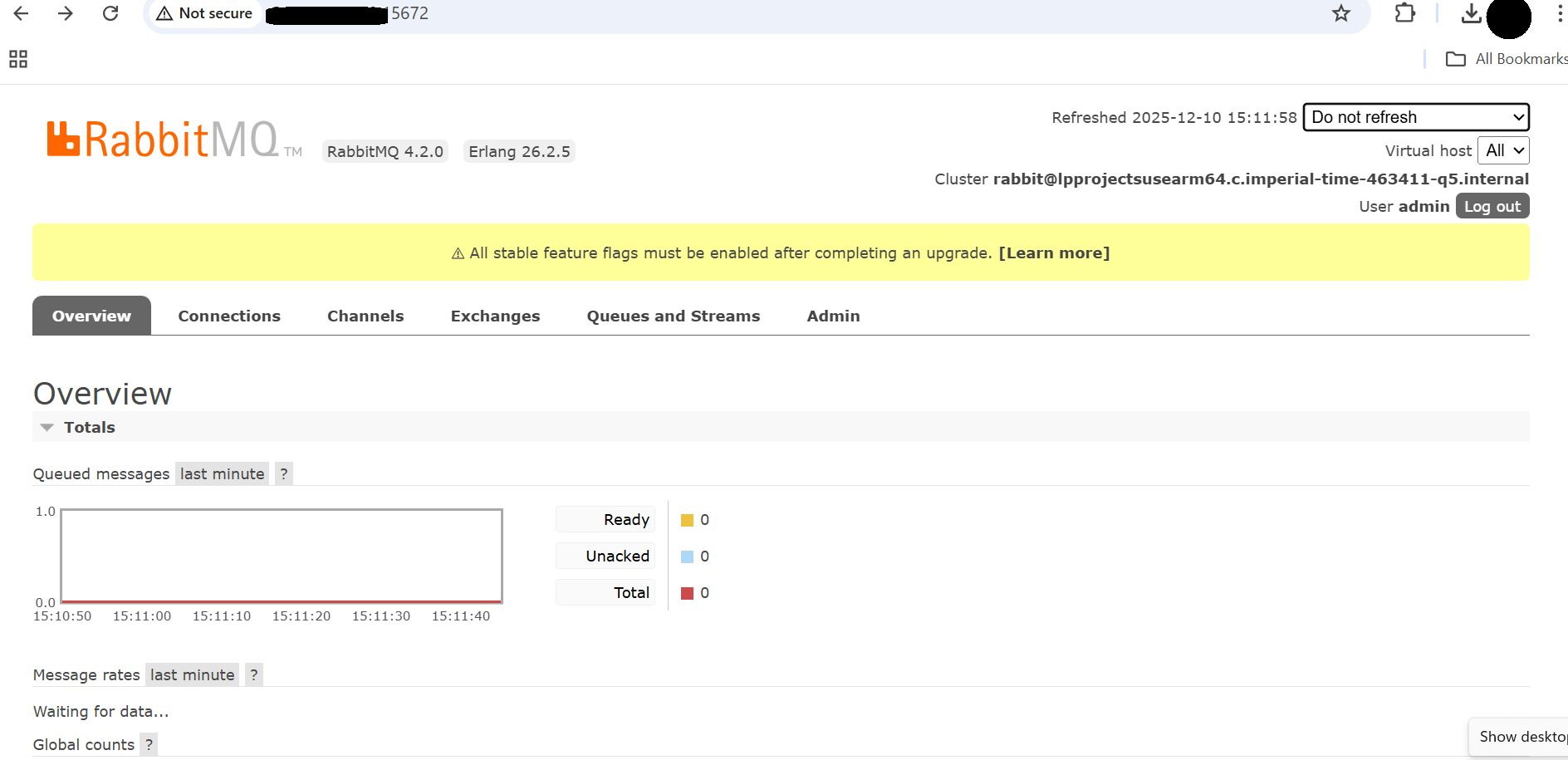 RabbitMQ Login page
RabbitMQ Login page
What you’ve accomplished and what’s next
You’ve successfully installed RabbitMQ on your Google Cloud Arm64 VM with:
- Erlang and RabbitMQ Server installed via RPM packages
- RabbitMQ Management UI enabled and accessible
- Administrative user configured for UI access
Next, you’ll validate your RabbitMQ installation and verify it’s functioning correctly.
This confirms that your RabbitMQ management dashboard is operational.
What you’ve accomplished and what’s next
You’ve successfully installed RabbitMQ on a Google Cloud SUSE Arm64 virtual machine, enabled the management plugin, created an admin user, and verified access to the web-based management interface. Next, you’ll validate the RabbitMQ installation with baseline messaging tests to ensure all components are functioning correctly.