Simulate OpenBMC and UEFI pre-silicon on Neoverse RD-V3
Introduction
What are OpenBMC and UEFI?
Set up the development environment for OpenBMC and UEFI
Run OpenBMC and host UEFI simulation on RD-V3 FVP
Monitor and control the host CPU using OpenBMC SOL and web UI
Customize IPMI commands in OpenBMC
Next Steps
Simulate OpenBMC and UEFI pre-silicon on Neoverse RD-V3
Access the host console via OpenBMC SOL
OpenBMC provides Serial oOer LAN (SOL) so you can access the host console (RD-V3 FVP) remotely through the BMC without a physical serial cable. In this section, you create a virtual UART bridge with socat, verify the port mappings, and open the host console from the BMC web UI.
Step 1: Connect the BMC and host consoles
Run this command on the Linux machine where the simulation is running to bridge the BMC and host UART ports:
socat -x tcp:localhost:5005 tcp:localhost:5067
This command connects the host-side UART port 5005 to the BMC-side port 5067 to enable bidirectional serial communication.
If you see a Connection refused error, check the FVP logs to verify the port numbers:
- In
fvp_boot.log, look for a line like: terminal_ns_uart0: Listening for serial connection on port 5005 - In
obmc_boot.log, confirm the corresponding line: terminal_3: Listening for serial connection on port 5067
Ensure both ports are active and match the socat command arguments.
Step 2: Manually set the host power state
After the SOL bridge is established, run the following command from the OpenBMC console shell to simulate the host as powered on:
busctl set-property xyz.openbmc_project.State.Host /xyz/openbmc_project/state/host0 xyz.openbmc_project.State.Host CurrentHostState s xyz.openbmc_project.State.Host.HostState.Running
This command updates the BMC internal host state so UEFI can begin execution.
Step 3: Access the host console from the web UI
From your simulation host, launch a browser and open the BMC Web UI at: https://127.0.0.1:4223
 BMC web UI login
BMC web UI loginLogin using the default credentials:
- Username: root
- Password: 0penBmc
Note As a reminder, the first character of the password is the number 0, not a capital O.
From the Overview page, click the
SOL Consolebutton. Web UI overview
Web UI overviewThe SOL terminal in the Web UI will display the host console output (UEFI shell or Linux login). You can type commands directly as if you were connected over a physical serial line.
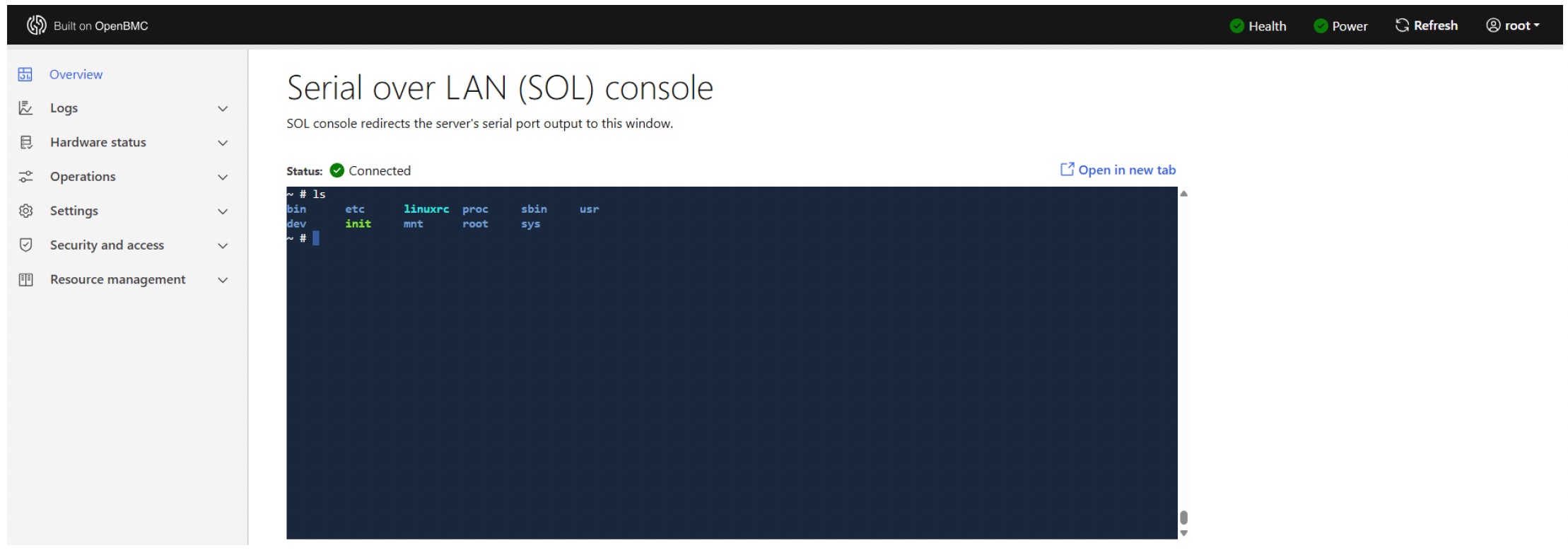 Web UI SOL console
Web UI SOL console
When you are connected to the SOL terminal, you can monitor the UEFI boot sequence, interact with the host shell, and run diagnostic or recovery workflows just as you would over a physical serial port.
This process confirms that OpenBMC manages host power and console access in your simulated environment.
In the next section, you extend this control by sending IPMI commands to the BMC to test low-level system interactions and implement custom OEM command handlers.