Deploy SqueezeNet 1.0 INT8 model with ONNX Runtime on Azure Cobalt 100
Introduction
Overview
Create an Arm-based Azure Cobalt 100 virtual machine
ONNX Installation
Baseline Testing
Benchmark ONNX runtime performance with onnxruntime_perf_test
Next Steps
Deploy SqueezeNet 1.0 INT8 model with ONNX Runtime on Azure Cobalt 100
Set up your Arm-based Azure Cobalt 100 virtual machine
There is more than one way to create an Arm-based Cobalt 100 virtual machine:
- The Microsoft Azure portal
- The Azure CLI
- Your preferred infrastructure as code (IaC) tool
In this Learning Path, you will use the Azure portal to create a virtual machine with the Arm-based Azure Cobalt 100 processor.
You will focus on the general-purpose virtual machines in the D-series. For further information, see the Microsoft Azure guide for the Dpsv6 size series .
While the steps to create this instance are included here for convenience, for further information on setting up Cobalt on Azure, see Deploy a Cobalt 100 virtual machine on Azure Learning Path .
Create an Arm-based Azure Virtual Machine
To launch an Arm-based virtual machine on Azure, you will use the Azure portal to create a Linux VM powered by the Cobalt 100 processor. This process is similar to creating any other Azure VM, but you will specifically select the Arm64 architecture and the D-Series v6 (D4ps_v6) size for optimal performance on Arm.
Follow these steps to deploy a Linux-based Azure Cobalt 100 VM:
- Select Create, and click on Virtual Machine from the drop-down list.
- Inside the Basic tab, fill in the instance details such as Virtual machine name and Region.
- Choose the image for your virtual machine (for example, Ubuntu Pro 24.04 LTS) and select Arm64 as the VM architecture.
- In the Size field, click on See all sizes and select the D-Series v6 family of virtual machines. Select D4ps_v6 from the list.
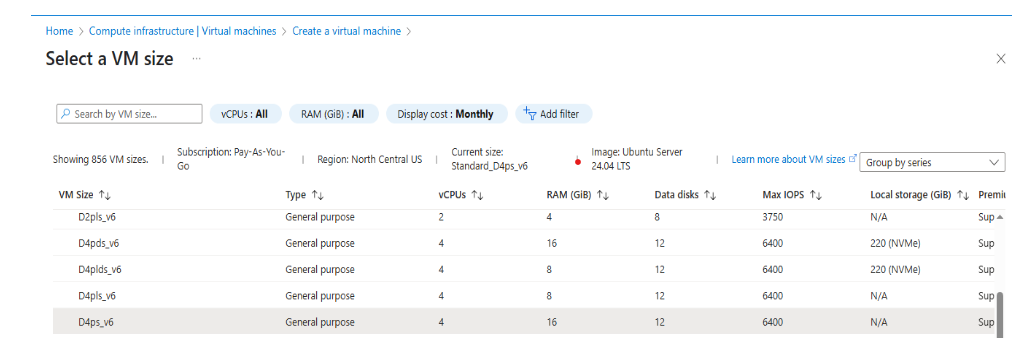 Select the D-Series v6 family of virtual machines
Select the D-Series v6 family of virtual machines
- Select SSH public key as an Authentication type. Azure will automatically generate an SSH key pair for you and allow you to store it for future use. It is a fast, simple, and secure way to connect to your virtual machine.
- Fill in the Administrator username for your VM.
- Select Generate new key pair, and select RSA SSH Format as the SSH Key Type. RSA could offer better security with keys longer than 3072 bits. Give a Key pair name to your SSH key.
- In the Inbound port rules, select HTTP (80) and SSH (22) as the inbound ports.
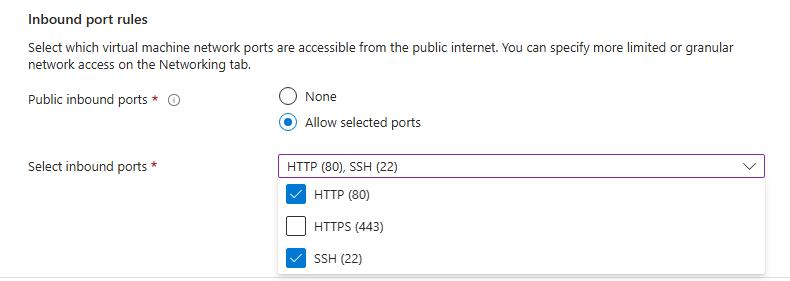 Allow inbound port rules
Allow inbound port rules
Click on the Review + Create tab and review the configuration for your virtual machine. It should look like the following:
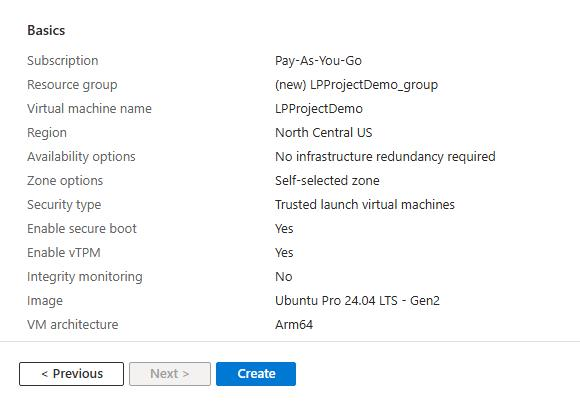 Review and Create an Azure Cobalt 100 Arm64 VM
Review and Create an Azure Cobalt 100 Arm64 VM
When you are confident about your selection, click on the Create button, and click on the Download Private key and Create Resources button.
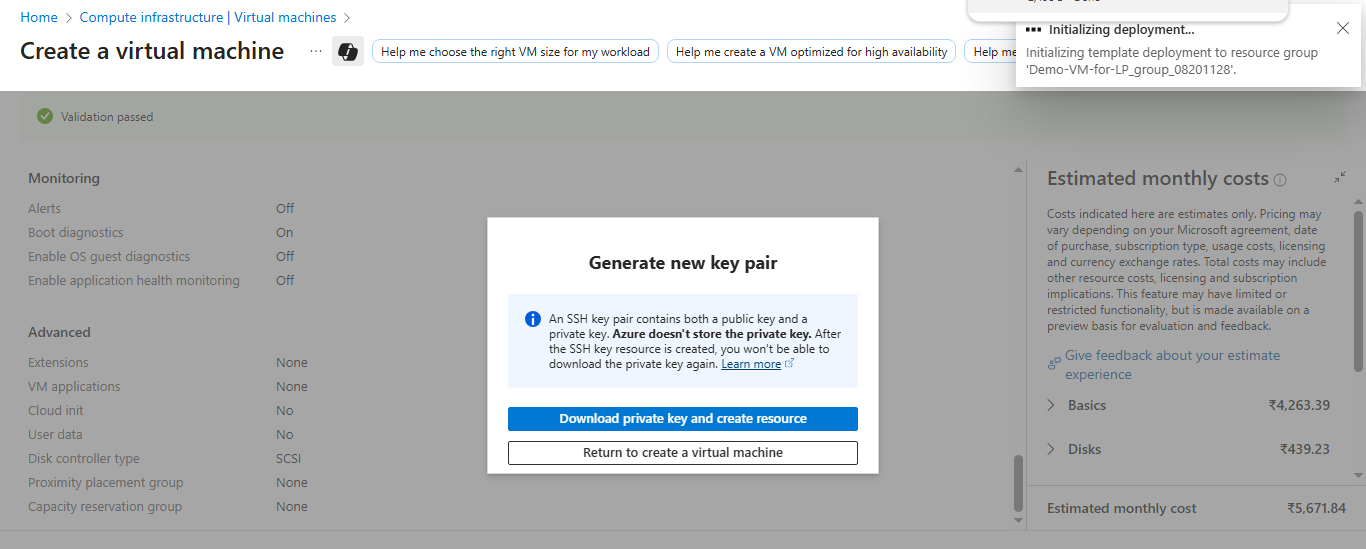 Download Private key and Create Resources
Download Private key and Create Resources
Your virtual machine should be ready and running within a few minutes. You can SSH into the virtual machine using the private key, along with the Public IP details.
You should see your Arm-based Azure Cobalt 100 VM listed as Running in the Azure portal. If you have trouble connecting, double-check your SSH key and ensure the correct ports are open. If the VM creation fails, check your Azure quota, region availability, or try a different VM size. For more troubleshooting tips, see the Deploy a Cobalt 100 virtual machine on Azure Learning Path .
Nice work! You have successfully provisioned an Arm-based Azure Cobalt 100 virtual machine. This setup is ideal for deploying Linux workloads, running ONNX Runtime, and benchmarking machine learning models on Arm64 infrastructure. You are now ready to continue with ONNX Runtime installation and performance testing in the next steps.
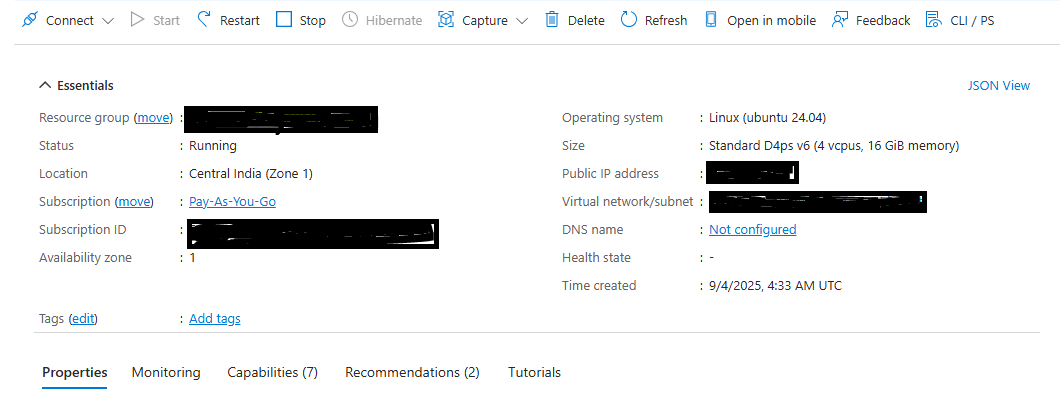 VM deployment confirmation in Azure portal
VM deployment confirmation in Azure portal
For further information or alternative setup options, see “Getting Started with Microsoft Azure” in Get started with Arm-based cloud instances .