Add Arm nodes to your GKE cluster using a multi-architecture Ollama container image
Introduction
Create the GKE Cluster
Deploy Ollama amd64 to the cluster
Deploy Ollama arm64 to the cluster
Test functionality and performance
Next Steps
Add Arm nodes to your GKE cluster using a multi-architecture Ollama container image
Add the arm64-pool node pool
You now have a workload running on an amd64 cluster and and can now evaluate the benefits of migrating to Arm.
This section shows you how to add an Arm-based node pool to the cluster, and apply an Ollama Arm deployment and service, mirroring what you did with the previous amd64 setup.
To add Arm nodes to the cluster:
- From the Clusters menu, select ollama-on-multiarch.
- Select Add node pool.
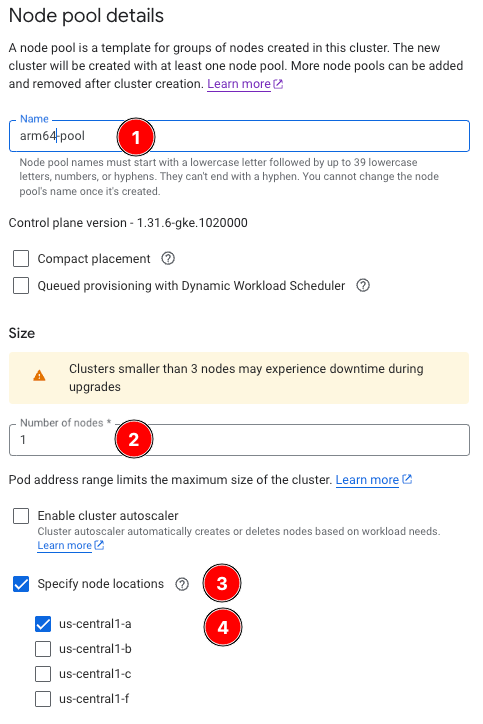
- For Name, enter
arm64-pool. - For Size, enter
1. - Check Specify node locations and select us-central1-a.
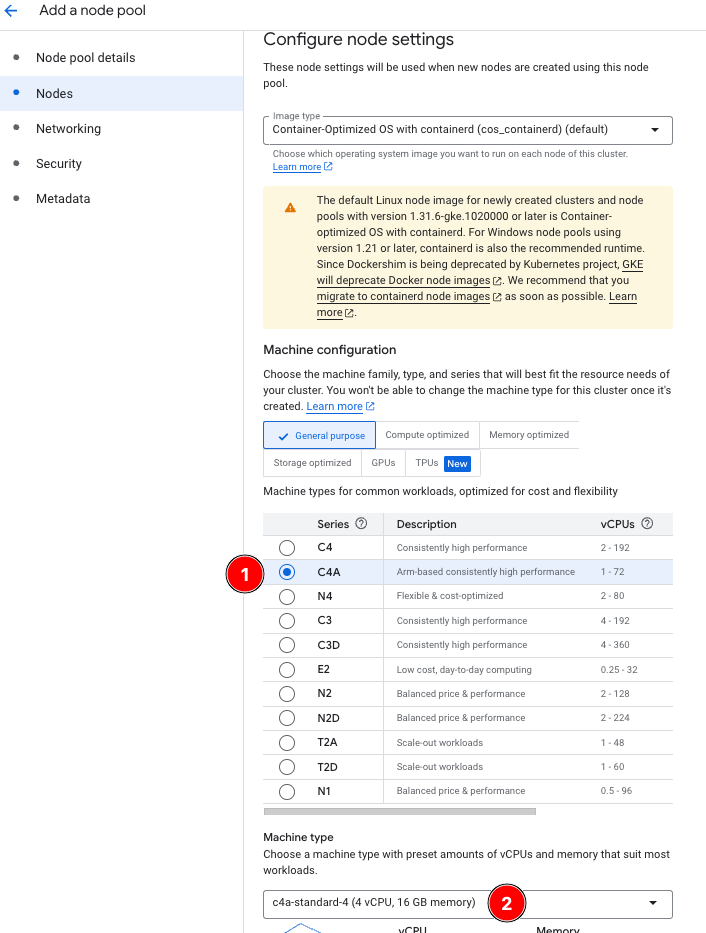
- Select the Nodes tab to navigate to the Configure node settings screen.
- Select C4A : c4a-standard-4 for Machine Configuration/Type.
To compare amd64 and arm64 performance, the c4a-standard-4 is used as the arm64 equivalent of the previously-deployed c4-standard-8 in the amd64 node pool.
- Select Create.
- After provisioning completes, select the newly-created arm64-pool from the Clusters screen to take you to the Node pool details page.
Notice the default NoSchedule taint applied by GKE to Arm nodes with arch=arm64:
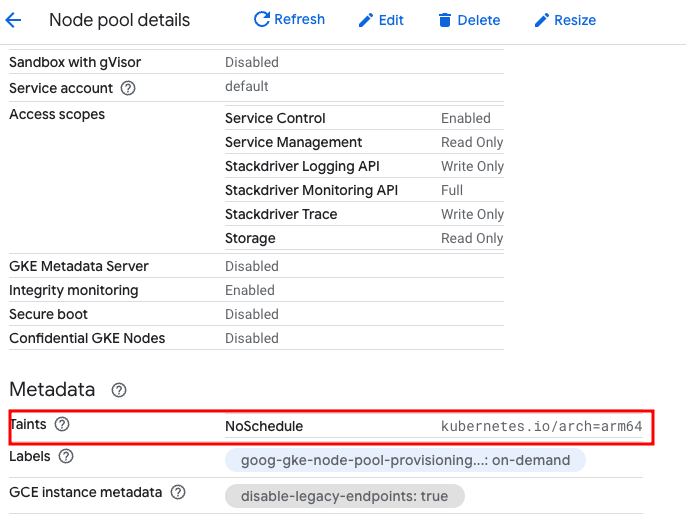
Without a toleration for this taint, you won’t be able to schedule any workloads on it. The nodeSelector in the amd64 (and as you will shortly see, the arm64) deployment YAMLs not only defines which architecture to target, but in the arm64 use case , it also adds the required toleration automatically.
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
Deployment and service
You can now apply the arm64-based deployment.
- Use a text editor to copy the following YAML, and save it to a file called
arm64_ollama.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ollama-arm64-deployment
labels:
app: ollama-multiarch
namespace: ollama
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
arch: arm64
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ollama-multiarch
arch: arm64
spec:
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/arch: arm64
containers:
- image: ollama/ollama:0.6.1
name: ollama-multiarch
ports:
- containerPort: 11434
name: http
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /root/.ollama
name: ollama-data
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: ollama-data
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ollama-arm64-svc
namespace: ollama
spec:
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- nodePort: 30666
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 11434
selector:
arch: arm64
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ollama-multiarch-svc
namespace: ollama
spec:
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- nodePort: 30667
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 11434
selector:
app: ollama-multiarch
type: LoadBalancer
When the above is applied:
- A new Deployment called
ollama-arm64-deploymentis created. Like the amd64 deployment, it pulls the same multi-architecture image from DockerHub.
Of particular interest is the nodeSelector kubernetes.io/arch, with the value of arm64. This ensures that the deployment runs on arm64-based nodes, utilizing the arm64 layer of the Ollama multi-architecture container image. The nodeSelector triggers the automatic creation of the toleration for the arm64 nodes.
- Two new load balancer services are created. The first,
ollama-arm64-svcis created, analogous to the existing service, and targets all pods with thearch: arm64label (the arm64 deployment creates these pods). The second service,ollama-multiarch-svc, targets all pods, regardless of the architecture. This service shows how you can mix and match pods in production to serve the same application regardless of node/pod architecture.
A sessionAffinity tag is added to this service to remove sticky connections to the target pods. This removes persistent connections to the same pod on each request.
Apply the arm64 deployment and service
- Run the following command to apply the arm64 deployment and service definitions:
kubectl apply -f arm64_ollama.yaml
You see the following responses:
deployment.apps/ollama-arm64-deployment created
service/ollama-arm64-svc created
service/ollama-multiarch-svc created
- Get the status of the nodes, pods, and services by running the following:
kubectl get nodes,pods,svc -nollama
Your output is similar to the following, showing two nodes, two pods, and three services:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node/gke-ollama-on-arm-amd64-pool-62c0835c-93ht Ready <none> 91m v1.31.6-gke.1020000
node/gke-ollama-on-arm-arm64-pool-2ae0d1f0-pqrf Ready <none> 4m11s v1.31.6-gke.1020000
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ollama-amd64-deployment-cbfc4b865-msftf 1/1 Running 0 29m
pod/ollama-arm64-deployment-678dc8556f-956d6 1/1 Running 0 2m52s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/ollama-amd64-svc LoadBalancer 1.2.3.4 1.2.3.4 80:30668/TCP 29m
service/ollama-arm64-svc LoadBalancer 1.2.3.4 1.2.3.4 80:30666/TCP 2m52s
service/ollama-multiarch-svc LoadBalancer 1.2.3.4 1.2.3.4 80:30667/TCP 2m52s
When the pods show Running and the service shows a valid External IP, you are ready to test the Ollama arm64 service.
Test the Ollama web service on arm64
To test the service, use the previously created model_util.sh from the previous section.
Replace the amd64 parameter with arm64:
- Run the following to make an HTTP request to the arm64 ollama service on port 80:
./model_util.sh arm64 hello
You get back the HTTP response, as well as the log line from the pod that served it:
Server response:
Using service endpoint 34.44.135.90 for hello on arm64
Ollama is running
Pod log output:
[pod/ollama-arm64-deployment-678dc8556f-956d6/ollama-multiarch] 2025-03-25T21:25:21.547384356Z
If you see the message “Ollama is running,” you have successfully set up your GKE cluster with both amd64 and arm64 nodes, each running a deployment using the Ollama multi-architecture container.
Continue to the next section to analyze the performance.