How can I connect my Python extension with GitHub Copilot?
For development, you can use ngrok to connect your extension to Copilot.
ngrok is a tool that creates a secure tunnel to your localhost, allowing you to expose a local server to the internet. This is useful for testing and development purposes.
How do I install and configure ngrok?
Follow the steps below to set up ngrok.
Download and install ngrok
If required, create a new account.
Refer to the Setup & installation section for installation details.
If you are using a Debian-based Linux system, run the command:
curl -sSL https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com/ngrok.asc \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ngrok.asc >/dev/null \
&& echo "deb https://ngrok-agent.s3.amazonaws.com buster main" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ngrok.list \
&& sudo apt update \
&& sudo apt install ngrok
Configure your ngrok account
Before you can start the ngrok server, you need an Authtoken.
If you don’t currently have one, create a new Authtoken from the Authtoken Get Started section .
Once you have the token, add it to the Linux computer where you are running your Python extension.
Substitute your token in the command below where it states <your-authtoken>:
ngrok config add-authtoken <your-authtoken>
ngrok is easier to use if you create a domain name. Go to the Domains section and add a new randomly generated domain name. You can create one domain name in a free account.
Use the domain name in the next section to start the server.
Start your local server
In a terminal, run the ngrok command to start the server.
Substitute your domain name in the command below to start the server on port 3000.
ngrok http --domain=your-domain.ngrok-free.app 3000
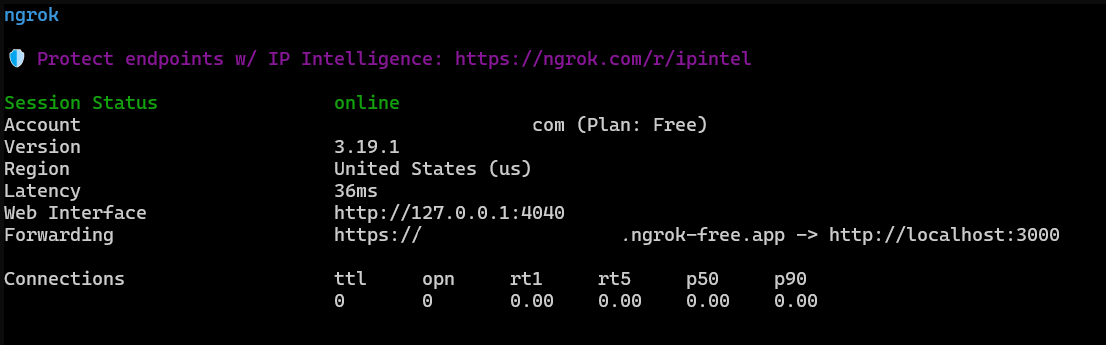
In the next section, you will use the public URL of your domain to configure a GitHub App in your GitHub account.