Deploy a containerized application using Azure Container Instances
Introduction
Azure Container Instances
Access the application
Deploying a Docker container from the Azure Container Registry
Next Steps
Deploy a containerized application using Azure Container Instances
Objective
In this section, you will deploy the Docker container from the Azure Container Registry to the Azure Container Instances. First, you must configure the Azure Container Registry to enable an Admin account as this is required by the Azure Container Instance.
Deployment
Under the Azure Portal, open the Cloud Shell. To do so, click on the Cloud Shell icon located in the top right corner of the Azure Portal:
In the Cloud Shell, type:
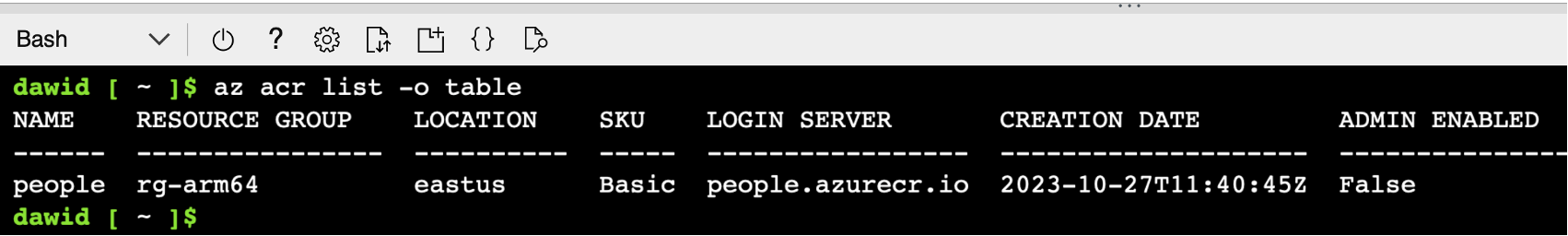
az acr list -o table
This command will display the list of container registries. Look for the ADMIN ENABLED column to ensure that the people registry has an Admin account disabled:
Now, you enable the Admin account:
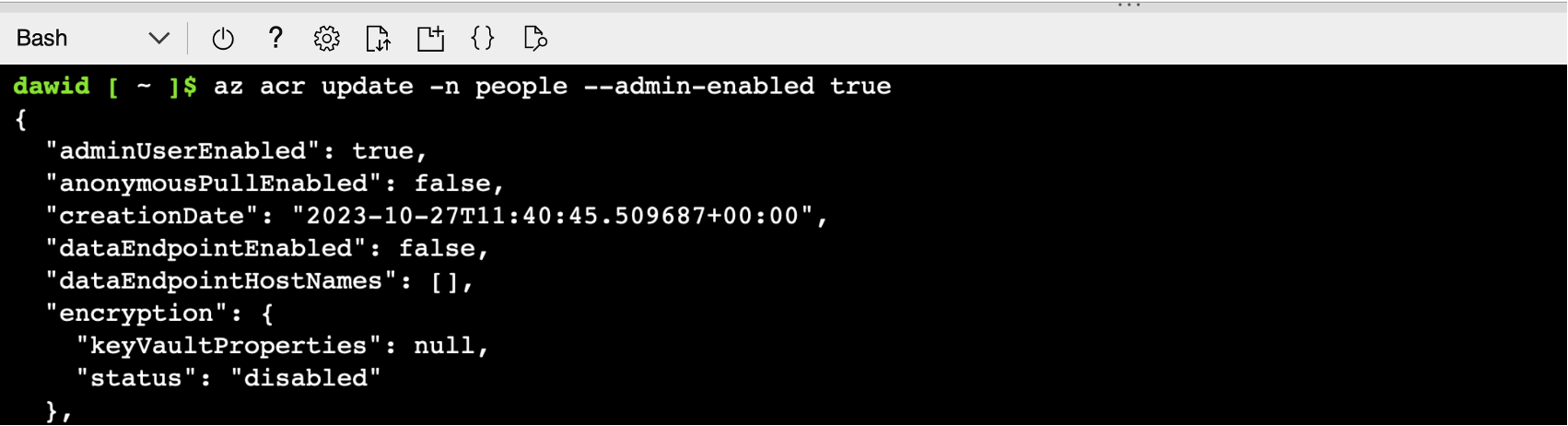
az acr update -n people --admin-enabled true
The command will generate the following output:
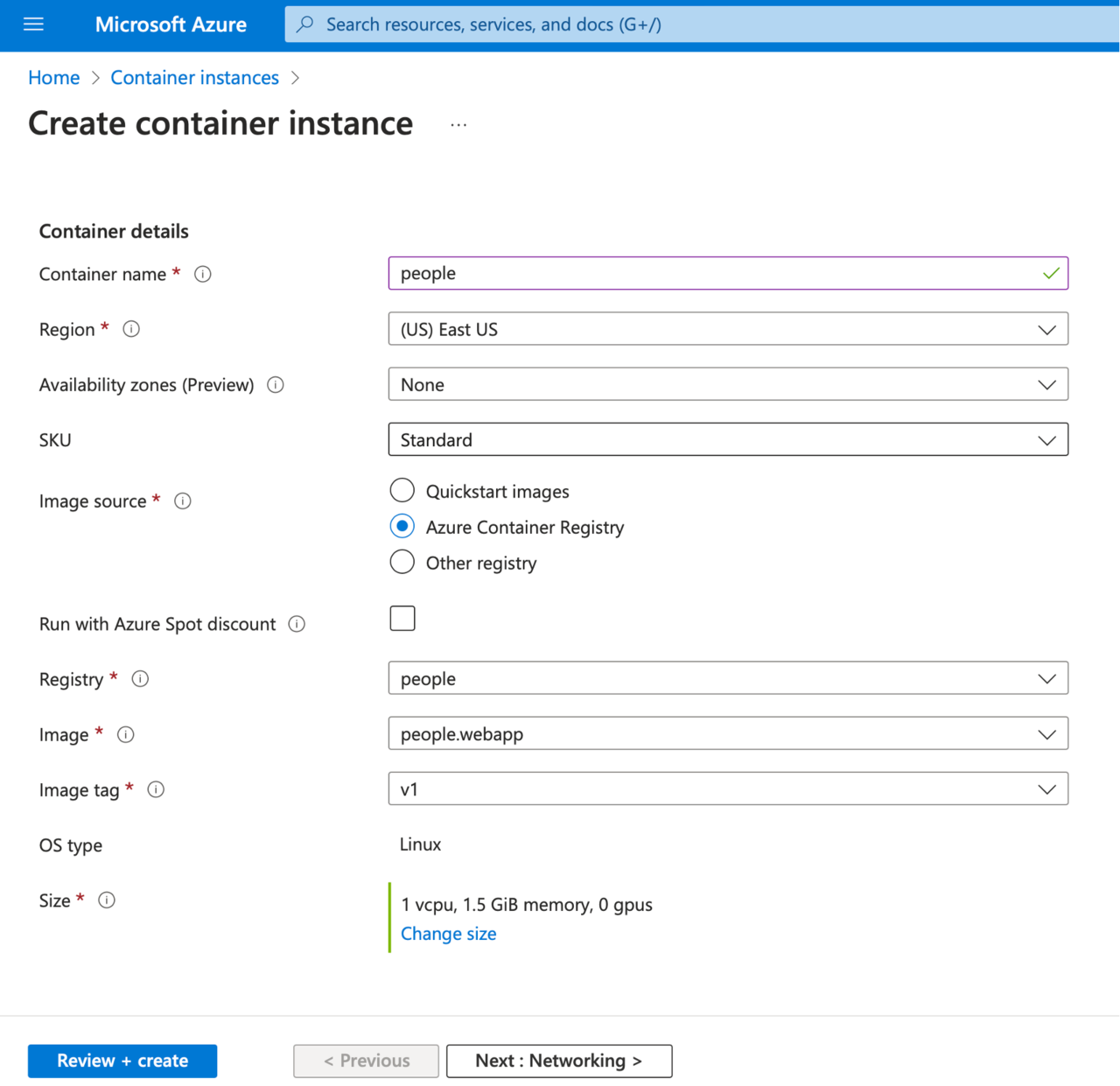
You can now create another Azure Container Instance. To do this, go to the Azure Container Instances and click the + Create button. Then configure an instance as follows:
- Subscription: Select your subscription
- Resource group: rg-arm64 (create a new group, if needed)
- Container name: people
- Region: East US (or select the region close to your location)
- Availability zones: None
- SKU: Standard
- Image source: Azure Container Registry
- Run with Azure Spot Discount: Unchecked
- Registry: people
- Image: people.webapp
- Image tag: v1
- OS type: Linux
- Size: 1 vcpu, 1.5 GiB memory, 0 gpus (or choose any other size, if this specific size is unavailable in the Azure region you used)
Click the Review + create button. Wait for the validation to complete, and then click the Create button.
The container will be created. However, it will not run as the Azure Container Instance is not yet compatible with arm64 containers. To verify the container status, open the Containers tab of the newly created Azure Container Instance:
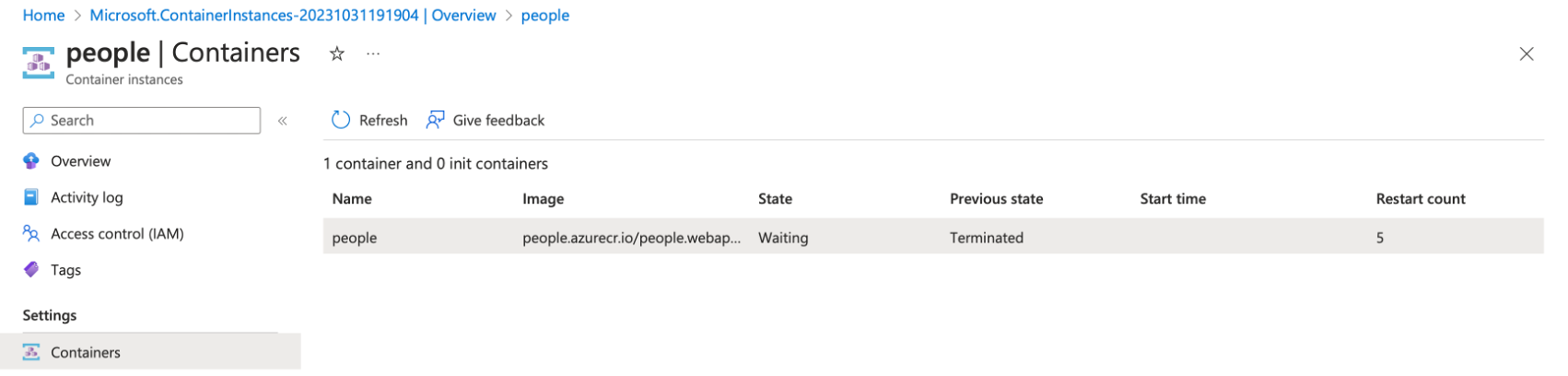
Compare this status with the aspnet-sample container instance you created before.
Summary
This tutorial has taught you how to deploy containerized applications using the Azure Container Instances. You deployed a Docker container from a public registry (Microsoft Container Registry) and a private registry (created with the Azure Container Registry). Along the way, you also learned how to configure the Azure Container Registry to enable such deployments.