Deploy Django on Arm-based Google Cloud C4A
Introduction
Get started with Django on Google Axion C4A
Configure firewall rules for Django on Google Cloud
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on GCP
Install Django on your Arm-based VM
Verify Django installation and run the development server
Deploy Django on GKE Axion with managed data services
Build a Django REST API with PostgreSQL and Redis
Containerize and deploy Django on Axion GKE
Benchmark Django application performance on Arm
Next Steps
Deploy Django on Arm-based Google Cloud C4A
Introduction
Get started with Django on Google Axion C4A
Configure firewall rules for Django on Google Cloud
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on GCP
Install Django on your Arm-based VM
Verify Django installation and run the development server
Deploy Django on GKE Axion with managed data services
Build a Django REST API with PostgreSQL and Redis
Containerize and deploy Django on Axion GKE
Benchmark Django application performance on Arm
Next Steps
Provision a Google Axion C4A Arm VM
In this section you’ll create a Google Axion C4A Arm-based virtual machine on Google Cloud Platform. You’ll use the c4a-standard-4 machine type, which provides 4 vCPUs and 16 GB of memory. This VM will host your Django application.
For help with GCP setup, see the Learning Path Getting started with Google Cloud Platform .
Provision a Google Axion C4A Arm VM in Google Cloud Console
To create a virtual machine based on the C4A instance type:
- Navigate to the Google Cloud Console .
- Go to Compute Engine > VM Instances and select Create Instance.
- Under Machine configuration:
- Populate fields such as Instance name, Region, and Zone.
- Set Series to
C4A. - Select
c4a-standard-4for machine type.
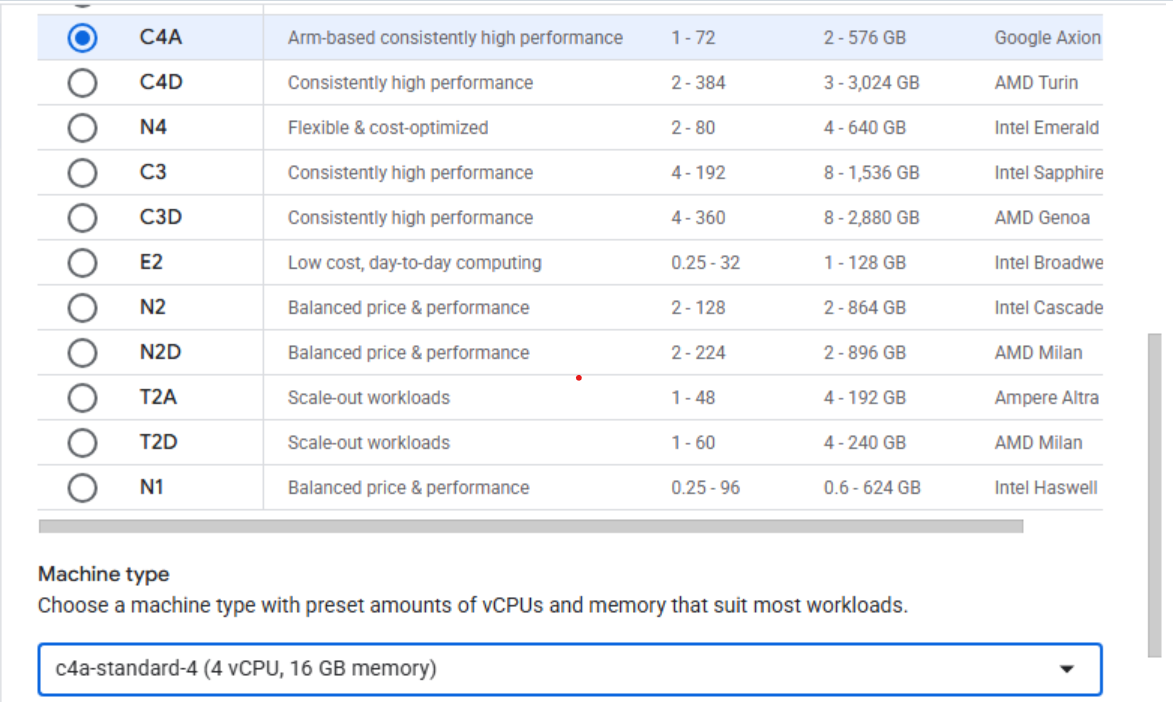 Configuring machine type to C4A in Google Cloud Console
Configuring machine type to C4A in Google Cloud Console
- Under OS and Storage, select Change, then choose an Arm64-based OS image. For this Learning Path, use SUSE Linux Enterprise Server.
- If using use SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. Select “Pay As You Go” for the license type.
- Once appropriately selected, please Click Select.
- Under Networking, enable Allow HTTP traffic.
- Also under Networking, in the “Network tags” text field add “allow-tcp-8000” as an additional tag
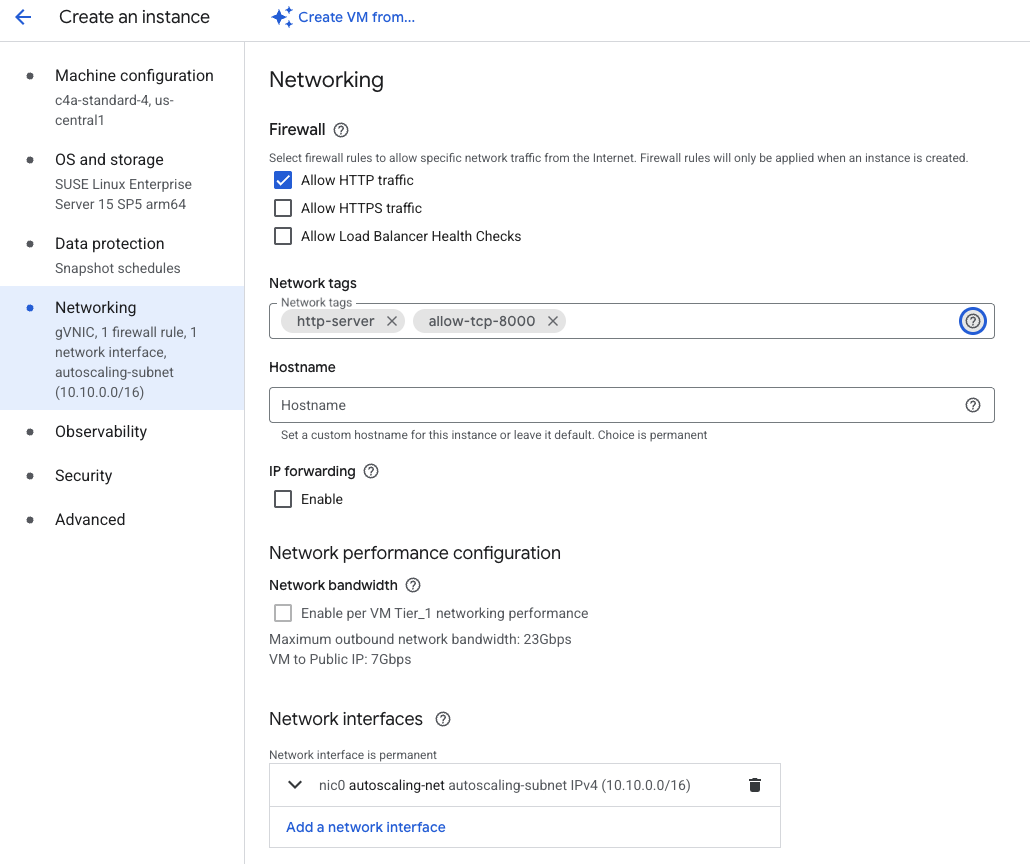 Configuring networking and tags
Configuring networking and tags
Create the instance
Click Create to launch your VM instance.
Google Cloud provisions the instance, which typically takes one to two minutes. Once the instance is running, you’ll see it listed in the VM instances table with a green checkmark.
Connect using SSH
Click the SSH button next to your running instance to open a browser-based terminal session.
 Launching an SSH session from the VM instances list
Launching an SSH session from the VM instances list
A browser window opens with a terminal shell connected to your VM. You’re now ready to install Django.
 Terminal shell connected to your VM
Terminal shell connected to your VM
What you’ve accomplished and what’s next
In this section, you provisioned a Google Axion C4A Arm VM and connected to it using SSH.
Next, you’ll install Django and the required dependencies on your VM.