Deploy Django on Arm-based Google Cloud C4A
Introduction
Get started with Django on Google Axion C4A
Configure firewall rules for Django on Google Cloud
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on GCP
Install Django on your Arm-based VM
Verify Django installation and run the development server
Deploy Django on GKE Axion with managed data services
Build a Django REST API with PostgreSQL and Redis
Containerize and deploy Django on Axion GKE
Benchmark Django application performance on Arm
Next Steps
Deploy Django on Arm-based Google Cloud C4A
Introduction
Get started with Django on Google Axion C4A
Configure firewall rules for Django on Google Cloud
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on GCP
Install Django on your Arm-based VM
Verify Django installation and run the development server
Deploy Django on GKE Axion with managed data services
Build a Django REST API with PostgreSQL and Redis
Containerize and deploy Django on Axion GKE
Benchmark Django application performance on Arm
Next Steps
Open port 8000 for your Django application
Before you can access your Django development server from your browser, you need to configure Google Cloud’s firewall to allow inbound traffic on port 8000. This section walks you through creating a firewall rule that permits HTTP requests to reach your VM.
For support on GCP setup, see the Learning Path Getting started with Google Cloud Platform .
Create a firewall rule in Google Cloud Console
Navigate to the Google Cloud Console and create a new firewall rule:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Select VPC network > Firewall.
- Select Create firewall rule.
 Google Cloud Console Firewall page
Google Cloud Console Firewall page
Configure the firewall rule
Fill in the rule details to allow traffic on port 8000:
- Set Name to
allow-tcp-8000. - Select your network (the default is
default; your organization may use a different network). - Set Direction of traffic to Ingress.
- Set Action on match to Allow.
- Set Targets to Specified target tags.
- Enter
allow-tcp-8000in the Target tags field. - Set Source IPv4 ranges to
0.0.0.0/0(allows traffic from any IP address; restrict this in production).
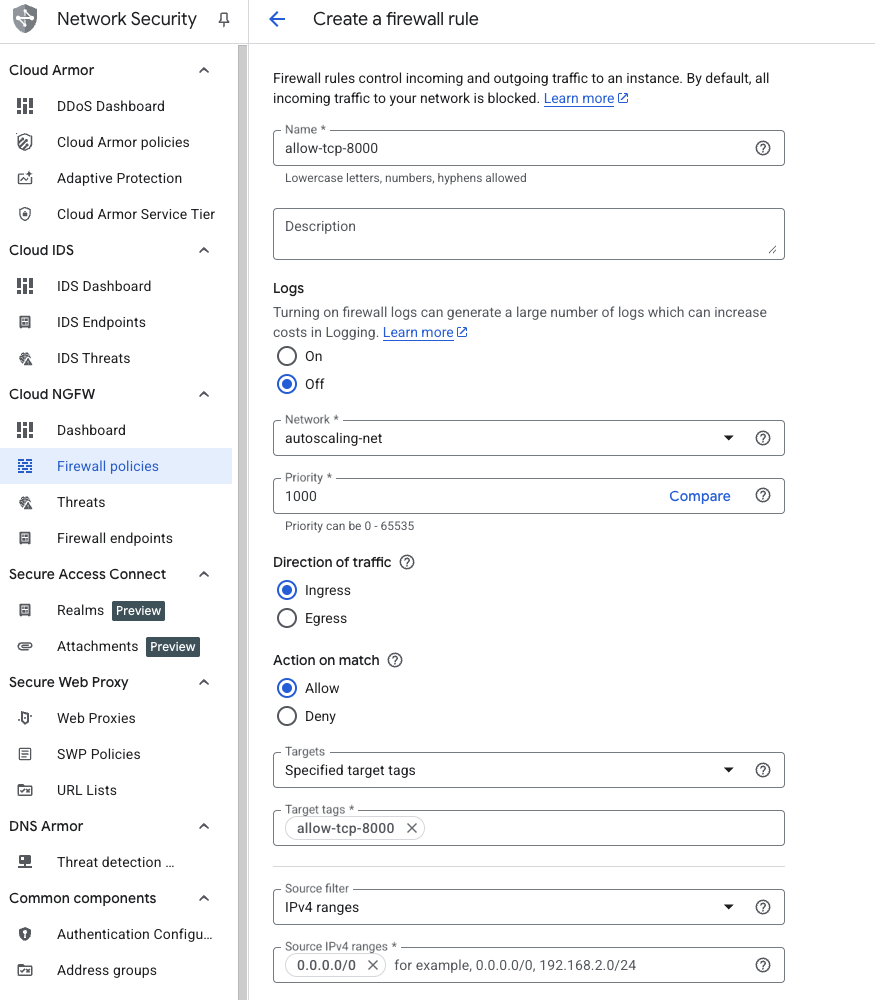 Firewall rule configuration
Firewall rule configuration
Specify the port and protocol
Configure the protocol and port settings:
- Under Protocols and ports, select Specified protocols and ports.
- Check the TCP checkbox.
- Enter
8000in the Ports field. - Click Create.
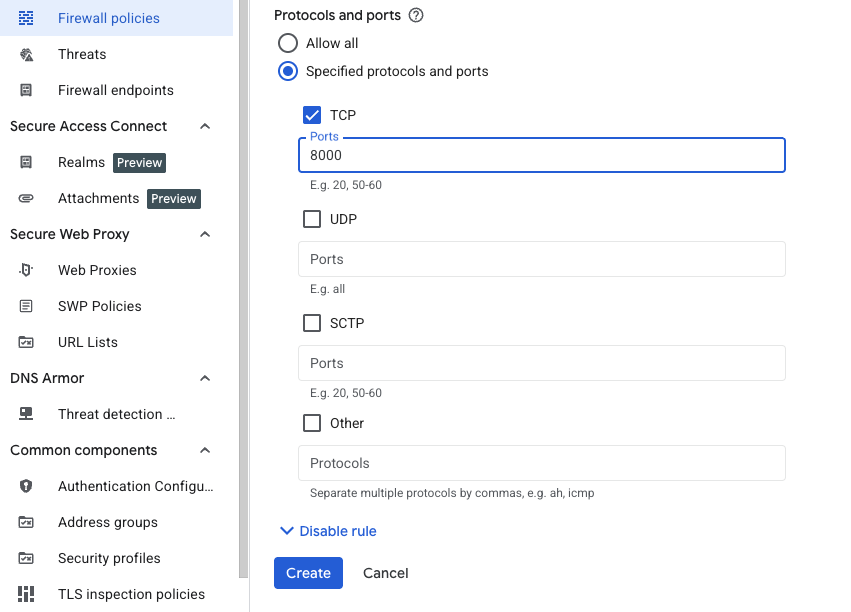 Specifying TCP port 8000
Specifying TCP port 8000
What you’ve accomplished and what’s next
In this section, you configured firewall rules to allow external HTTP traffic on port 8000, making your Django application accessible from the internet.
Next, you’ll provision a Google Axion C4A Arm VM to host your Django application.