Overview
This section guides you through benchmarking Couchbase performance on a GCP SUSE Arm64 VM using the official cbc-pillowfight tool from Couchbase C SDK. It involves installing dependencies, building the SDK, verifying the setup, and running the benchmark test.
Install build tools and dependencies
Before compiling the Couchbase SDK, install all the required development tools and libraries:
sudo zypper install -y gcc gcc-c++ cmake make git openssl-devel libevent-devel cyrus-sasl-devel java
Download and build the Couchbase C SDK (includes cbc-pillowfight)
To get the benchmarking tools, download the official Couchbase C SDK source code. This SDK provides both the cbc command-line client and the cbc-pillowfight benchmarking utility.
First, move to your home directory and clone the repository:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/couchbase/libcouchbase.git
cd libcouchbase
Next, build and install the SDK:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make -j$(nproc)
sudo make install
This process compiles the SDK and installs the binaries to /usr/local/bin. You can now use cbc and cbc-pillowfight for benchmarking Couchbase performance on your Arm64 VM. cbc-pillowfight is a Couchbase command-line benchmarking tool that simulates a workload by performing concurrent read and write operations on a bucket to test Couchbase cluster performance.
Now clone the official Couchbase C SDK repository from GitHub. This SDK includes benchmarking tools such as cbc and cbc-pillowfight:
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/couchbase/libcouchbase.git
cd libcouchbase
To build and install, use the following:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make -j$(nproc)
sudo make install
Update the dynamic linker configuration
After installing the Couchbase C SDK, you need to update the dynamic linker configuration so your system can locate the Couchbase libraries. Add the library path to the linker configuration file:
echo "/usr/local/lib" | sudo tee /etc/ld.so.conf.d/libcouchbase.conf
Next, refresh the linker cache to apply the changes:
sudo ldconfig
This step ensures that applications can find and use the Couchbase libraries installed on your Arm64 VM. After installation, tell the system where to find the Couchbase libraries:
echo "/usr/local/lib" | sudo tee /etc/ld.so.conf.d/libcouchbase.conf
Then refresh the linker cache to make the libraries available system-wide:
sudo ldconfig
Verify installation
After installation, the tools such as cbc and cbc-pillowfight should be available in /usr/local/bin.
Verify this with:
cbc version
cbc-pillowfight --help
For the cbc version command, you should see an output similar to:
cbc:
Runtime: Version=3.3.18, Changeset=a8e17873d167ec75338a358e54cec3994612d260
Headers: Version=3.3.18, Changeset=a8e17873d167ec75338a358e54cec3994612d260
Build Timestamp: 2025-11-06 04:36:42
CMake Build Type: Release
Default plugin directory: /usr/local/lib64/libcouchbase
IO: Default=libevent, Current=libevent, Accessible=libevent,select
SSL Runtime: OpenSSL 1.1.1l-fips 24 Aug 2021 SUSE release 150500.17.40.1
SSL Headers: OpenSSL 1.1.1l-fips 24 Aug 2021 SUSE release SUSE_OPENSSL_RELEASE
HAVE_PKCS5_PBKDF2_HMAC: yes
Snappy: 1.1.8
Tracing: SUPPORTED
System: Linux-6.4.0-150600.23.73-default; aarch64
CC: GNU 7.5.0; -fno-strict-aliasing -ggdb3 -pthread
CXX: GNU 7.5.0; -fno-strict-aliasing -ggdb3 -pthread
For the cbc-pillowfight --help command, you should see the help menu for cbc-pillowfight displayed. The output is similar to:
cbc-pillowfight - Simulate workload for Couchbase buckets
Usage: cbc-pillowfight [options]
Options:
-U <connstr> Connection string to Couchbase bucket
-u <username> Couchbase admin username
-P <password> Couchbase admin password
-I <num> Number of items (documents)
-B <num> Batch size for operations
-t <num> Number of concurrent threads
-c <num> Number of operation cycles
--help Show this help message and exit
Run Benchmark using cbc-pillowfight
Once Couchbase Server is running and you’ve created a bucket (for example, benchmark), you’re ready to test performance. Run the following command, replacing password with your Couchbase Administrator password:
cbc-pillowfight -U couchbase://127.0.0.1/benchmark \
-u Administrator -P password -I 10000 -B 1000 -t 5 -c 500
- -U couchbase://127.0.0.1/benchmark: Connection string to Couchbase bucket
- -u Administrator: Couchbase admin username (default: “Administrator”)
- -P password: Couchbase Administrator’s password
- -I 10000: Number of items (documents) to use
- -B 1000: Batch size for operations
- -t 5: Number of concurrent threads
- -c 500: Number of operation cycles to run
You should see an output similar to:
Running. Press Ctrl-C to terminate...
Thread 0 has finished populating.
Thread 1 has finished populating.
Thread 2 has finished populating.
Thread 3 has finished populating.
Thread 4 has finished populating.
Monitor Couchbase performance in real time
While the benchmark is running, open the Couchbase web console in your browser by entering the following address, replacing <your-vm-ip> with your VM’s IP address:
http://<your-vm-ip>:8091
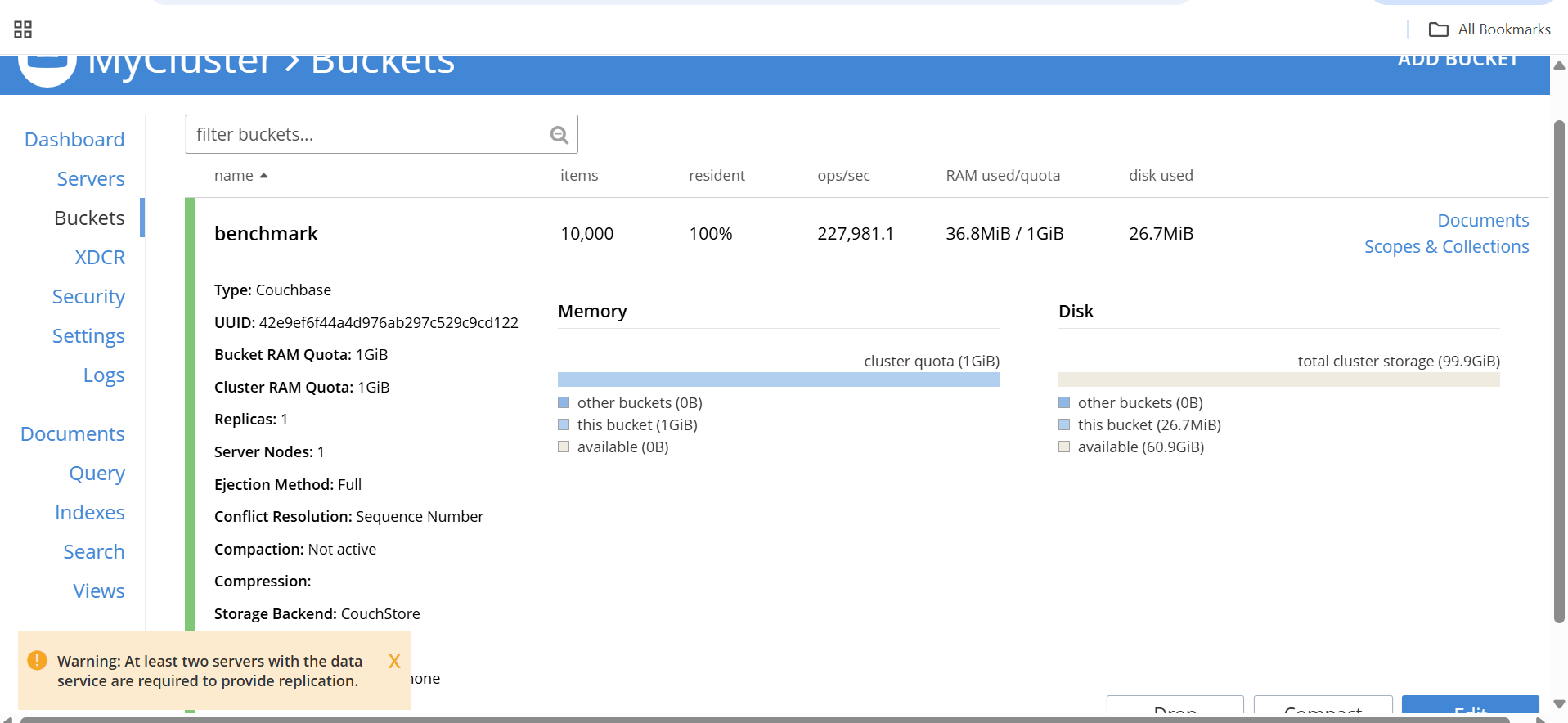
Select Dashboard, then Buckets, and choose the benchmark bucket. Here, you can observe live performance metrics, including:
- Ops/sec: Number of operations per second, which should closely match the CLI output from
cbc-pillowfight. - Resident ratio: Percentage of data served from memory, indicating memory efficiency.
- Disk write queue: Number of pending write operations, useful for spotting disk bottlenecks.
- CPU and memory usage: Shows how effectively Arm cores are handling the workload.
Monitoring these metrics helps you validate Couchbase performance and resource utilization on your Arm64 VM.
 Monitor Benchmark Log
Monitor Benchmark Log
Benchmark results on Arm64 VM
The following table summarizes the benchmark results from running cbc-pillowfight on a c4a-standard-4 (4 vCPU, 16 GB memory) Arm64 VM in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) with SUSE Linux:
| Name | Items | Resident | Ops/sec | RAM Used / Quota | Disk Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| benchmark | 10,000 | 100% | 227,981.1 | 36.8 MiB / 1 GiB | 26.7 MiB |
The key takeaways here are:
- The benchmark achieved a throughput of 227,981.1 operations per second, demonstrating strong performance on Arm64.
- The 100 percent resident ratio indicates that all data was served from memory, which minimized disk access.
- Resource usage remained low, with only 36.8 MiB of RAM and 26.7 MiB of disk consumed, both well within the allocated quotas.
- Overall, Couchbase on this Arm64 VM delivered efficient, high-speed operations while using minimal resources.
You can use these results as a baseline for further tuning or to compare with other VM sizes and configurations.