Deploy CircleCI Arm Native Workflows on AWS EC2 Graviton
Introduction
Get Started with CircleCI on AWS Graviton
Create an AWS EC2 Arm64 Graviton Instance
Install CircleCI CLI
Create a resource class in CircleCI
Install CircleCI machine runner on AWS Graviton
Verify CircleCI Arm64 Self-Hosted runner
Next Steps
Deploy CircleCI Arm Native Workflows on AWS EC2 Graviton
Verify CircleCI Arm64 Self-Hosted Runner
This section walks you through validating your self-hosted CircleCI runner on an Arm64 machine by executing a simple workflow and a test computation. This ensures your runner is correctly configured and ready to process jobs.
Create a test repository
Start by creating a GitHub repository dedicated to verifying your Arm64 runner:
git clone https://github.com/<your-username>/aws-circleci/
cd aws-circleci
This repository serves as a sandbox to confirm that your CircleCI runner can pick up and run jobs for Arm64 workflows.
Add a sample script
Create a minimal shell script to confirm your runner can execute commands:
echo 'echo "Hello from CircleCI Arm64 Runner!"' > hello.sh
chmod +x hello.sh
This script prints a message when run, helping you verify that your self-hosted runner is working as expected.
echo 'echo "Hello from CircleCI Arm64 Runner!"' > hello.sh
chmod +x hello.sh
Define the CircleCI Configuration
The next step is to add a .circleci/config.yml file to define the workflow that will run on your Arm64 runner. Start by creating the directory in your new repository.
mkdir .circleci
Then enter the YAML content:
version: 2.1
jobs:
test-Arm64:
machine:
enabled: true
resource_class: circleci/arm64 # Replace with your actual resource class
steps:
- checkout
- run:
name: Verify Arm64 Runner
command: |
uname -m
lscpu | grep Architecture
./hello.sh
- run:
name: Run sample computation
command: |
echo "Performing test on Arm64 runner"
echo "CPU Info:"
lscpu
echo "Success!"
workflows:
test-workflow:
jobs:
- test-Arm64
In the snippet above, you need to replace the resource_class variable with the name you defined in the previous section.
This snippet:
- Defines a single job
test-Arm64using a machine executor on a self-hosted Arm64 runner. - Checks CPU architecture with
uname -mandlscputo verify the runner. - Executes a simple script
hello.shto confirm the runner can run commands. - Runs a sample computation step to display CPU info and print.
Commit and Push to GitHub
When the files you created (hello.sh, .circleci/config.yml) are ready, push your project to GitHub so CircleCI can build and verify the Arm64 runner automatically.
git add .
git commit -m "Initial CircleCI Arm64 test"
If you haven’t already, you need to configure your GitHub credentials before pushing. Once that is done, run the following to upstream your changes:
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
After pushing your code to GitHub, open your CircleCI Dashboard → Projects, and confirm that your test-Arm64 workflow starts running using your self-hosted runner.
If everything is set up correctly, you’ll see your job running under the resource class you created.
Output
Once the job starts running, CircleCI does the following:
It verifies the Arm64 Runner:
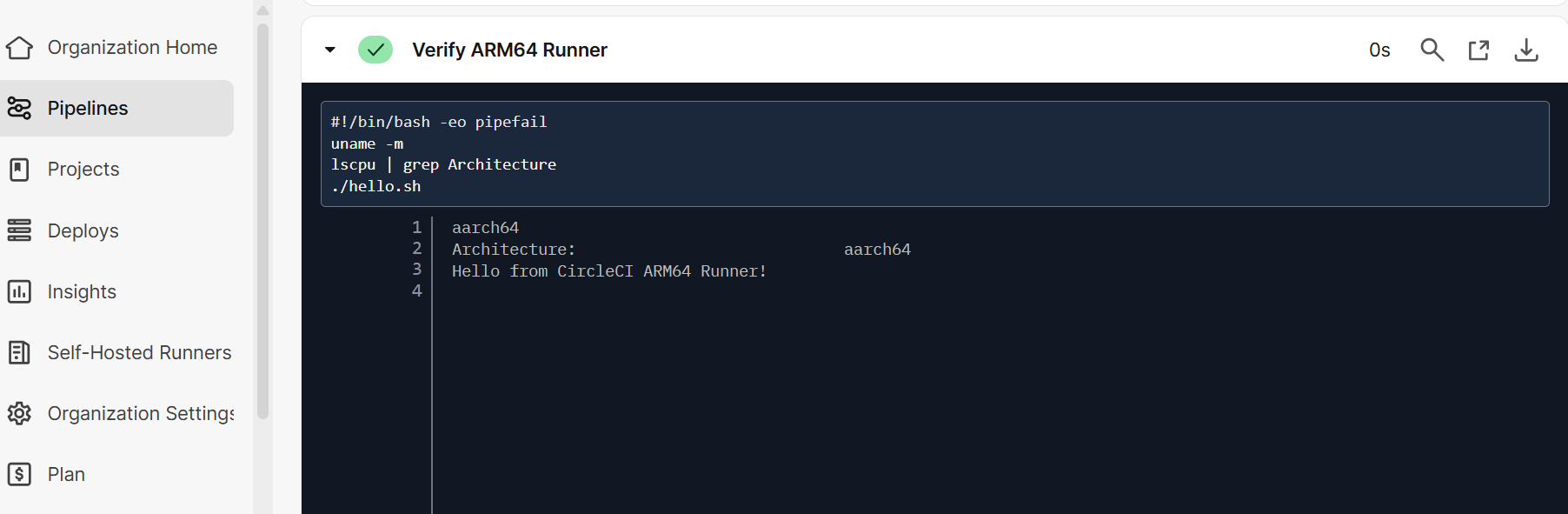 Self-Hosted Runners
Self-Hosted RunnersIt runs a sample computation:
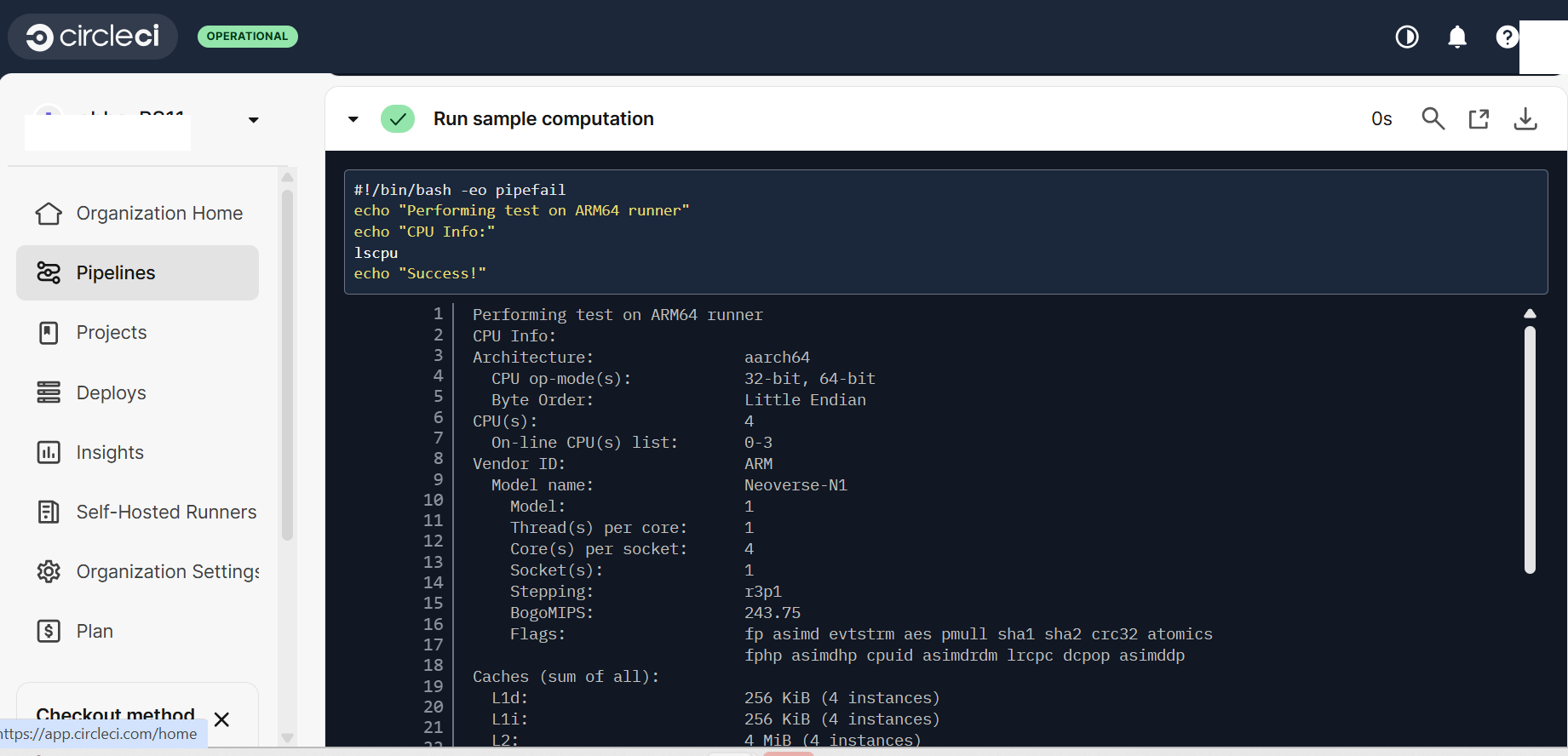 Self-Hosted Runners
Self-Hosted Runners
All CircleCI jobs have run successfully, the sample computation completed, and all outputs are visible in the CircleCI Dashboard.