Deploy Cassandra on a Google Axion C4A virtual machine
Introduction
Get started with Cassandra on Google Axion C4A
Create a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine
Install Apache Cassandra
Test Cassandra baseline functionality
Benchmark Cassandra performance
Next Steps
Deploy Cassandra on a Google Axion C4A virtual machine
Overview
This section shows you how to provision a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) using the c4a-standard-4 (4 vCPUs, 16 GB memory) machine type in the Google Cloud Console.
For support on GCP setup, see the Learning Path Getting started with Google Cloud Platform .
Provision a Google Axion C4A Arm VM
To create a virtual machine based on the C4A instance type:
Navigate to the Google Cloud Console .
Go to Compute Engine > VM Instances and select Create Instance.
Under Machine configuration:
- Populate fields such as Instance name, Region, and Zone.
- Set Series to
C4A. - Select
c4a-standard-4for machine type.
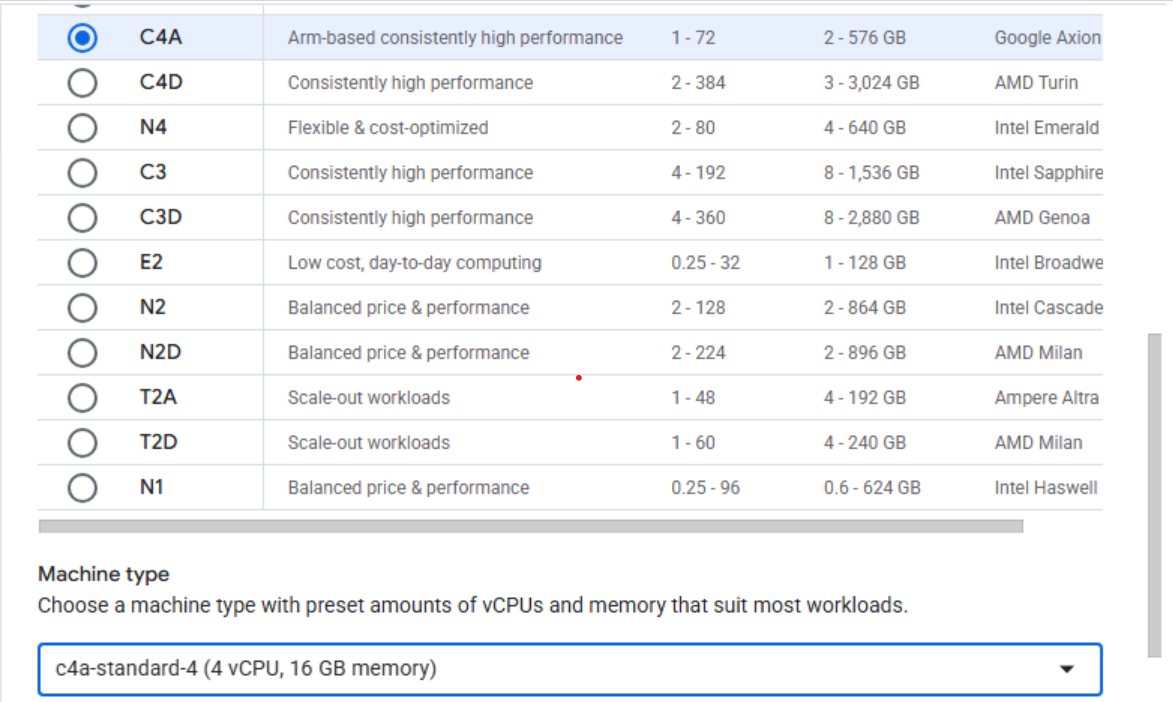 Creating a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine in Google Cloud Console
Creating a Google Axion C4A Arm virtual machine in Google Cloud ConsoleUnder OS and Storage, select Change, then choose an Arm64-based OS image. For this Learning Path, use SUSE Linux Enterprise Server or Ubuntu.
- If using SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, select “Pay As You Go” for the license type.
- If using Ubuntu, under the Version tab, scroll down and select the aarch64 version of Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
Once appropriately selected, select Select.
Under Networking, enable Allow HTTP traffic.
Select Create to launch the instance.
Once created, you see an SSH option to the right in your list of VM instances. Select this to launch an SSH shell into your VM instance:
 SSH button in VM instances list
SSH button in VM instances list
- A browser window opens and displays a shell into your VM instance:
 Terminal shell in your VM instance
Terminal shell in your VM instance
Explore your instance: run uname
Use the uname utility to verify that you are using an Arm-based server. For example:
uname -m
The output identifies the host machine as aarch64.
Run hello world
Install the gcc compiler:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y build-essential
sudo zypper refresh
sudo zypper install -y gcc
Using a text editor of your choice, create a file named hello.c with the contents below:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
printf("hello world\n");
return 0;
}
Build and run the application:
gcc hello.c -o hello
./hello
The output is:
hello world
Automate Arm infrastructure deployment
Cloud infrastructure deployment is typically done via Infrastructure as Code (IaC) automation tools. There are Cloud Service Provider-specific tools like Google Cloud Deployment Manager .
There are also Cloud Service Provider-agnostic tools like Terraform . Review the Learning Path Deploy Arm virtual machines on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) using Terraform next.