Profile ONNX model performance with SME2 using KleidiAI and ONNX Runtime
Introduction
ONNX Runtime architecture with SME2 acceleration
Integration of KleidiAI to ORT MLAS
Build ONNX Runtime with KleidiAI and SME2 for Android
Profile ONNX model performance
Next Steps
Profile ONNX model performance with SME2 using KleidiAI and ONNX Runtime
Integration of KleidiAI to ONNX Runtime MLAS
ONNX Runtime automatically detects and uses KleidiAI when SME2 support is available:
- Detection: MLAS checks the CPU capabilities for SME2 support at runtime.
- Dispatch: when SME2 is detected, MLAS replaces its default kernels with KleidiAI micro-kernels. For example, a Gemm operation that normally uses NEON instructions dispatches to a KleidiAI SME2 micro-kernel instead.
Currently, KleidiAI in MLAS provides ArmKleidiAI::MlasConv, ArmKleidiAI::MlasGemmBatch, and ArmKleidiAI::MlasDynamicQGemmBatch kernels.
The ArmKleidiAI::MlasConv kernel
ORT dispatches 2D fp32 (32-bit floating point) convolution operators with batch_size=1 and multiple filters (filter kernel equal to or greater than (3,3)) to the ArmKleidiAI::MlasConv kernel.
For example, the figure below shows a (7,7) Conv node.
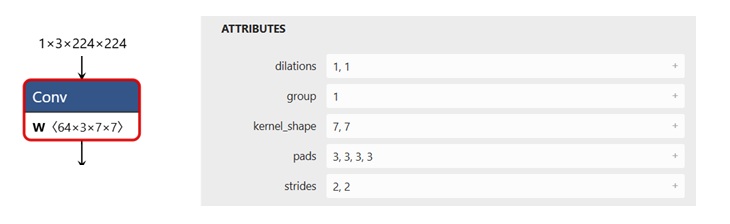 An example of a (7,7) Conv node
An example of a (7,7) Conv node
ArmKleidiAI::MlasConv kernel uses KleidiAI’s indirect matrix multiplication (imatmul) micro kernel to accelerate the convolution.
The function calls are shown as below.
onnxruntime::InferenceSession::Run
|--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraph
| |--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraphImp
| | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteThePlan
| | | |--onnxruntime::concurrency::ThreadPool::Schedule
| | | | |--onnxruntime::RunSince
| | | | | |--onnxruntime::LaunchKernelStep::Execute
| | | | | | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteKernel
| | | | | | | |--onnxruntime::Conv<float>::Compute
| | | | | | | | |--MlasConv
| | | | | | | | | |--ArmKleidiAI::MlasConv
| | | | | | | | | | |--ConvolveSme
| | | | | | | | | | | |--MlasTrySimpleParallel
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_lhs_imatmul_pack_x32p2vlx1_x32p_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_lhs_imatmul_pack_x32p2vlx1_x32p_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_rhs_imatmul_pack_kxn_x32p2vlx1b_x32_x32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_rhs_imatmul_pack_kxn_x32p2vlx1b_x32_x32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_imatmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1b_2vlx2vl_sme2_mopa
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_imatmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1b_2vlx2vl_sme2_mopa
The ArmKleidiAI::MlasGemmBatch kernel
This kernel performs a batched fp32 matrix multiplication (GEMM or GemV) operation using KleidiAI matmul micro kernels. fp32 Conv operators with (1,1) filter kernels also use this kernel.
For example, the figure below shows a (1,1) Conv node.
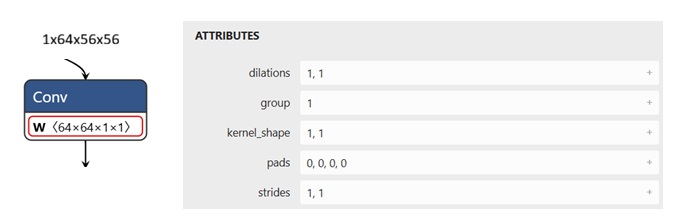 An example of a (1,1) FusedConv node
An example of a (1,1) FusedConv node
The function calls of fp32 Conv operators with (1,1) filter kernels are shown below.
onnxruntime::InferenceSession::Run
|--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraph
| |--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraphImp
| | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteThePlan
| | | |--onnxruntime::concurrency::ThreadPool::Schedule
| | | | |--onnxruntime::RunSince
| | | | | |--onnxruntime::LaunchKernelStep::Execute
| | | | | | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteKernel
| | | | | | | |--onnxruntime::Conv<float>::Compute
| | | | | | | | |--MlasConv
| | | | | | | | | |--MlasGemmBatch
| | | | | | | | | | |--ArmKleidiAI::MlasGemmBatch
| | | | | | | | | | | |--MlasTrySimpleParallel
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_lhs_pack_f32p2vlx1_f32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_lhs_pack_f32p2vlx1_f32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--ArmKleidiAI::MlasGemmPackB
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_rhs_pack_kxn_f32p2vlx1biasf32_f32_f32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_rhs_pack_kxn_f32p2vlx1biasf32_f32_f32_sme
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_matmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1biasf32_sme2_mopa
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_matmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1biasf32_sme2_mopa
For example, the figure below shows a Gemm node.
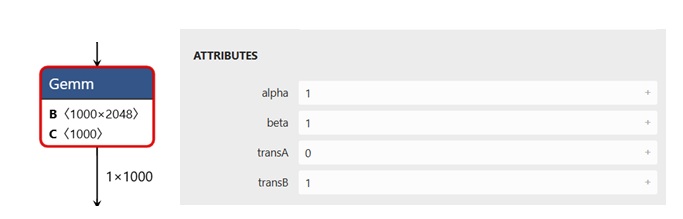 An example of a Gemm node
An example of a Gemm node
The function calls of fp32 Gemm operators are shown below.
onnxruntime::InferenceSession::Run
|--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraph
| |--onnxruntime::utils::ExecuteGraphImp
| | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteThePlan
| | | |--onnxruntime::concurrency::ThreadPool::Schedule
| | | | |--onnxruntime::RunSince
| | | | | |--onnxruntime::LaunchKernelStep::Execute
| | | | | | |--onnxruntime::ExecuteKernel
| | | | | | | |--onnxruntime::Gemm<float>::Compute
| | | | | | | | |--MlasGemm
| | | | | | | | | |--MlasGemmBatch
| | | | | | | | | | |--ArmKleidiAI::MlasGemmBatch
| | | | | | | | | | | |--MlasTrySimpleParallel
| | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_run_matmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1biasf32_sme2_mopa
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |--kai_kernel_matmul_clamp_f32_f32p2vlx1_f32p2vlx1biasf32_sme2_mopa
The ArmKleidiAI::MlasDynamicQGemmBatch kernel
This kernel performs matrix multiplication with float output of dynamically quantized A and symmetrically quantized B.
It uses the KleidiAI kai_kernel_matmul_clamp_f32_qai8dxp1vlx4_qsi8cxp4vlx4_1vlx4vl_sme2_mopa micro kernel.
What you’ve accomplished and what’s next
You now understand how KleidiAI integrates into ONNX Runtime’s MLAS backend and which operators benefit from SME2 acceleration. You’ve learned about the three main kernel types: MlasConv for convolution operations, MlasGemmBatch for matrix multiplications and 1x1 convolutions, and MlasDynamicQGemmBatch for quantized operations. You’ve also seen the complete function call stacks showing how ONNX Runtime dispatches to KleidiAI kernels.
Next, you’ll build ONNX Runtime with KleidiAI support enabled and prepare the benchmark tools for profiling on Android.