Build and run a letter recognition NN model on an STM32L4 Discovery board
Introduction
Prepare development environment
Collect training data
Train the model
Feature extraction
Run the model on development board
Next Steps
Build and run a letter recognition NN model on an STM32L4 Discovery board
Until now, you trained and tested the model with the raw accelerometer data.
Now, you are going to extract features from the data and train a model which makes prediction based on the extracted features.
Here, you are going to use the mean and standard deviation of each axis as features.
Extract features
First, extract the features from the collected dataset and save the features for training.
data_files = [file for file in os.listdir(samples_dir) if '.csv' in file]
stride = 30
slidingWindowExt = 6
feature_data = []
feature_labels = []
for idx, file in enumerate(data_files):
df = pd.read_csv(os.path.join(samples_dir, file))
x = df['X'].to_numpy()
y = df['Y'].to_numpy()
z = df['Z'].to_numpy()
for i in range(int(df.shape[0]/stride)):
base_idx = i * stride
# Mean feature
x_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(x[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
y_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(y[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
z_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(z[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
# STD feature
x_std_ext = np.array([np.std(x[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
y_std_ext = np.array([np.std(y[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
z_std_ext = np.array([np.std(z[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(base_idx, base_idx + stride, slidingWindowExt)])
batch = np.array([x_mean_ext, y_mean_ext, z_mean_ext, x_std_ext, y_std_ext, z_std_ext])
feature_data.append(batch)
feature_labels.append(idx)
print('Added {} data to the feature data list with label: {}'.format(file, idx))
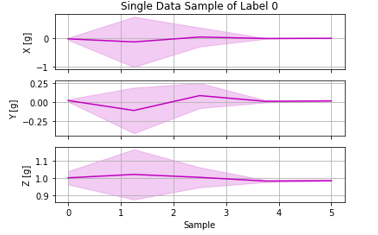
Plot features
You can check the extracted features with this code block. These are the extracted features from one data sample. Expected output shown below:
Feature based model
Create a new multi-layer perceptron model for the features. The new model has 1592 parameters because it uses a smaller input than the previous model. Train the model and check the accuracy.
x_train, y_train = sklearn.utils.shuffle(np.array(feature_data), np.array(feature_labels))
y_train = tf.keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, len(np.unique(y_train)))
data_shape = x_train[0].shape
model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.Input(shape=data_shape),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(data_shape[0] * data_shape[1], activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(20, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(len(np.unique(y_train)), activation="softmax")
]
)
model.summary()
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=32, epochs=500, validation_split=0.4)
You see the accuracy improved with the feature extraction. Test the new model with this code block to check if the model generates better results.
input('Press Enter once MCU is ready')
line = ser.readline()
lineList = convert_to_list(str(line))
new_df = convert_list_to_df(lineList)
print('New data acquired:\n', new_df.describe())
x = new_df['X'].to_numpy()
y = new_df['Y'].to_numpy()
z = new_df['Z'].to_numpy()
# Mean feature
x_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(x[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
y_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(y[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
z_mean_ext = np.array([np.mean(z[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
# STD feature
x_std_ext = np.array([np.std(x[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
y_std_ext = np.array([np.std(y[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
z_std_ext = np.array([np.std(z[i:i + slidingWindowExt]) for i in range(0, stride, slidingWindowExt)])
inf_data = np.array([x_mean_ext, y_mean_ext, z_mean_ext, x_std_ext, y_std_ext, z_std_ext])
# For inference, explicitly tell that the data has a batch size of 1
plot_single_feature_sample(data_sample=inf_data)
inf_data = inf_data.reshape((1, data_shape[0], data_shape[1]))
pred = model.predict(inf_data)
print('Model Prediction: ', np.argmax(pred))
Save the model
Finally, save the model by executing this code block.
with open('test.npy', 'wb') as f:
np.save(f, x_train)
with open('test_out.npy', 'wb') as f:
np.save(f, y_train)
model.save('feature_mlp.h5')