Automate Windows on Arm virtual machine deployment with QEMU and KVM on Arm Linux
Introduction
Check system requirements
Understand and customize Windows on Arm VM automation scripts
Create a Windows on Arm virtual machine
Run a Windows on Arm virtual machine
Next Steps
Automate Windows on Arm virtual machine deployment with QEMU and KVM on Arm Linux
Basic VM launch command
After your Windows 11 Arm VM is created, launching it is simple with the unified run script:
./run-win11-vm.sh $HOME/win11-vm
This single command handles the entire VM startup and connection process automatically.
The script performs three key steps. It does the following:
- Checks if the VM is already running
- Starts the VM in headless mode if required
- Connects you through RDP using Remmina
When the virtual machine starts you will see it on your Linux desktop:
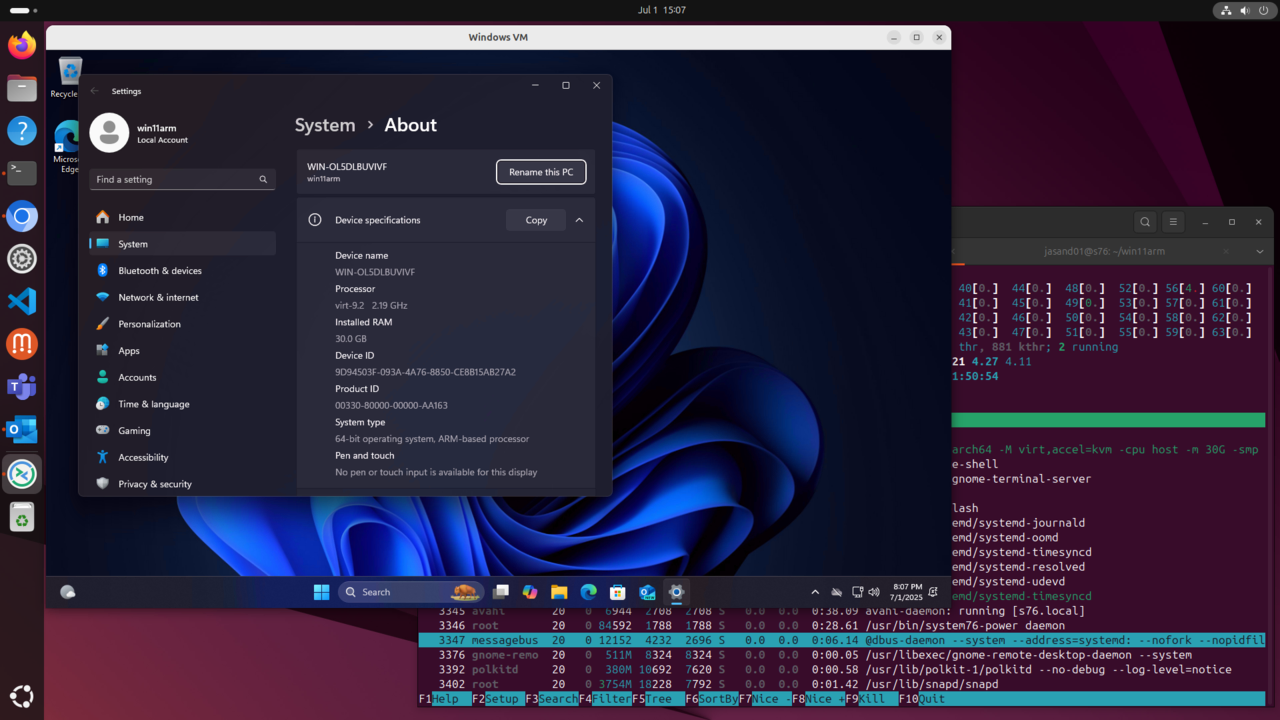 Windows 11 Arm VM desktop
Windows 11 Arm VM desktop
What does the run script do?
Understanding the run script flow helps you troubleshoot issues and customize the VM runtime behavior.
Step 1: Check if VM is already running
The script first checks if your VM is already running to avoid conflicts.
Here is a fragment of the code:
# Check for existing VM process
if [ -f "$vm_path/qemu.pid" ]; then
local vm_pid=$(cat "$vm_path/qemu.pid" 2>/dev/null)
if process_exists "$vm_pid"; then
status "VM is already running (PID: $vm_pid)"
fi
fi
The run script looks for the qemu.pid file in your VM directory, verifies the process ID is still active, cleans up stale PID files from previous sessions, and skips VM startup if already running.
If this happens you will see output similar to:
VM is already running (PID: 12345)
Waiting for RDP service on port 3389...
Step 2: Start VM in headless mode
If the VM isn’t running, the script starts it in headless mode (no GUI window) using QEMU.
The arguments to QEMU are shown below:
qemu-system-aarch64 \
-M virt,accel=kvm \
-cpu host \
-m ${vm_mem}G \
-smp $num_cores \
-name "Windows on Arm" \
-pidfile "$vm_path/qemu.pid" \
-display none \
-netdev user,id=nic,hostfwd=tcp:127.0.0.1:${rdp_port}-:3389 \
-device virtio-net-pci,netdev=nic \
-bios /usr/share/qemu-efi-aarch64/QEMU_EFI.fd \
-drive file="$vm_path/disk.qcow2",if=virtio,discard=unmap,aio=threads,cache=none \
-daemonize
The important arguments to QEMU are:
-M virt,accel=kvm- Uses ARM virtualization with KVM acceleration-cpu host- Passes through your host CPU features for best performance-display none- Runs headless (no QEMU window)-daemonize- Runs QEMU as a background daemon-netdev user,hostfwd=...- Sets up port forwarding for RDP access-pidfile- Creates a PID file for process management
The script automatically detects and allocates CPU and memory resources.
The code is shown below:
# Memory: Half of available RAM (minimum 2GB)
local total_ram_gb=$(awk '/MemTotal/ {print int($2/1048576)}' /proc/meminfo)
local vm_mem=$((total_ram_gb / 2))
[ "$vm_mem" -lt 2 ] && vm_mem=2
# CPU: Half of available cores (minimum 4)
local total_cores=$(grep -c ^processor /proc/cpuinfo)
local num_cores=$((total_cores / 2))
[ "$num_cores" -lt 4 ] && num_cores=4
When the run script executes, you will see the CPU and RAM allocated:
Starting Windows VM in headless mode...
Using 8GB RAM and 4 CPU cores
VM started successfully
Step 3: Connect via RDP
Once the VM is running, the script waits for the RDP service and connects automatically.
Here is the function which waits for the port to be ready:
# Wait for RDP service to be available
wait_for_rdp() {
local port="$1"
local max_attempts=60
while [ $attempt -le $max_attempts ]; do
if timeout 3 bash -c "echo >/dev/tcp/localhost/$port" 2>/dev/null; then
return 0
fi
sleep 2
attempt=$((attempt + 1))
done
}
Once the RDP service is ready, Remmina is started and connects.
The related output is shown below:
Waiting for RDP service on port 3389...
RDP service is available!
Connecting to VM via RDP (localhost:3389)...
Username: win11arm
Run script options and examples
The run script supports several options for different use cases:
Custom RDP port
./run-win11-vm.sh /path/to/vm --rdp-port 3390
Uses a custom RDP port, useful when running multiple VMs or avoiding port conflicts.
Help information
./run-win11-vm.sh --help
Displays usage information and all available options.
Remmina integration
The script uses Remmina as the RDP client and creates a Remmina profile with the connection settings.
The file name is connect.remmina and you can review and edit as needed.
[remmina]
name=VM Connect
protocol=RDP
scale=2
quality=9
disable_fastpath=0
glyph-cache=0
multitransport=0
relax-order-checks=1
ignore-tls-errors=1
cert_ignore=1
window_width=1024
window_height=768
window_maximize=0
disableautoreconnect=1
viewmode=1
network=lan #change viewmode=1 to viewmode=3 for fullscreen
sound=local #to get microphone input working, change to sound=remote, and USB passthrough your m
icrophone to the VM.
colordepth=63
VM shutdown
The preferred method is to shut down Windows normally from within the virtual machine.
- Click the Start button in Windows
- Select Power → Shut down
- Wait for Windows to complete shutdown
- VM automatically stops when Windows finishes shutting down
- Remmina exits automatically when the connection closes
You should avoid killing QEMU directly as it may corrupt the VM disk as well as avoid exiting Remmina as it may leave the VM running in the background.
Runtime monitoring and management
Checking VM status
To check if your VM is running without connecting:
# Check for VM process
ps aux | grep "Windows on Arm"
# Check PID file
cat $HOME/win11-vm/qemu.pid
# Test RDP connectivity
timeout 3 bash -c "echo >/dev/tcp/localhost/3389"
If the RDP connectivity fails the output is:
bash: connect: Connection refused
bash: line 1: /dev/tcp/localhost/3389: Connection refused
Resource usage monitoring
Monitor VM resource usage while running:
# CPU and memory usage
top -p $(cat $HOME/win11-vm/qemu.pid)
# Detailed process information
ps -p $(cat $HOME/win11-vm/qemu.pid) -o pid,ppid,cmd,%cpu,%mem,etime
Multiple VM management
Running multiple VMs requires different RDP ports:
# First VM (default port 3389)
./run-win11-vm.sh $HOME/vm1
# Second VM (custom port 3390)
./run-win11-vm.sh $HOME/vm2 --rdp-port 3390
# Third VM (custom port 3391)
./run-win11-vm.sh $HOME/vm3 --rdp-port 3391
Each VM needs its own directory and unique RDP port to avoid conflicts.
Troubleshooting runtime issues
RDP connection failures
If RDP connection fails:
Error: RDP service did not become available after 120 seconds
Check VM is actually running:
ps aux | grep qemu-system-aarch64
Verify RDP port:
netstat -tlnp | grep 3389
Known Remmina crash issue
When disconnecting from RDP, Remmina may crash with:
./run-win11-vm.sh: line 143: 60433 Aborted (core dumped) remmina -c "$remmina_file" $remmina_flags 2> /dev/null
RDP session ended
This is a known Remmina issue and does not affect VM functionality.
You have completed the VM execution section. You now know how to run, monitor, and manage Windows on Arm virtual machines on an Arm Linux system. Keep building your skills and explore more advanced automation or troubleshooting as your next step - great work!