Deploy firmware on hybrid edge systems using containers
Introduction
Motivation
Hybrid container runtime
AVH device setup
Deploy firmware container using `containerd`
Deploy SMARTER Demo using K3s
Building the hybrid-runtime and container image (optional)
Next Steps
Deploy firmware on hybrid edge systems using containers
K3s is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution, built to work well in embedded environments. It is optimized for Arm.
K3s setup
You will use a single node K3s cluster setup. To download K3s and set it up, run the following commands:
export INSTALL_K3S_EXEC="server --disable traefik --disable metrics-server --disable coredns --disable local-storage --flannel-backend=none --cluster-dns 169.254.0.2 --container-runtime-endpoint=unix://var/run/containerd/containerd.sock"
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | INSTALL_K3S_EXEC=$INSTALL_K3S_EXEC sh -s -
This can take a few minutes to complete.
Make sure K3s is running. A snippet of the expected output is shown below:
systemctl status k3s
* k3s.service - Lightweight Kubernetes
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/k3s.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since <date and time>
Docs: https://k3s.io
Main PID: 2069 (k3s-server)
Tasks: 13
Memory: 448.0M
CGroup: /system.slice/k3s.service
`-2069 "/usr/local/bin/k3s agent"
For things to work properly, you need to make K3s aware of the hybrid-runtime by configuring this with containerd. You can find the config file with the K3s example YAML files in GitHub.
Download the K3s demo example YAML files:
wget https://github.com/smarter-project/hybrid-runtime/releases/download/v1.5/example.tar.gz
Extract the files:
tar -xvf example.tar.gz
Create a containerd directory under /etc and copy the config file to there:
mkdir /etc/containerd
mv example/config.toml /etc/containerd/
Restart containerd, and make sure that it’s running:
systemctl restart containerd
systemctl status containerd
If you run the kubectl command below, you will see that the node is not ready:
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
narsil NotReady control-plane,master 18m v1.29.6+k3s2
To fix this, you need to apply a Container Network Interface (CNI). Run the command to use the smarter_cni, and label the node as follows:
kubectl apply -f example/smarter_cni.yaml
kubectl label node narsil smarter.cni=deploy
Re-run the kubectl command:
kubectl get nodes
This time, you should be able to see that the node is ready.
root@narsil:~#
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
narsil Ready control-plane,master 24m v1.29.6+k3s2
K3s demo
Deploy SMARTER camera demo
The smarter camera demo is used as an example to show the capabilities of K3s.
First, you need to set a runtimeClass in K3s. It allows you to select the container runtime we want to use:
kubectl apply -f example/runtime_class.yaml
Once this is done, we can run the smarter demo:
kubectl apply -f example/test_hybrid.yaml
The test_hybrid.yaml file contains the following:
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: example3
labels:
k3s-app: example3
spec:
runtimeClassName: hybrid
containers:
- name: example-hybrid-pod3
image: ghcr.io/smarter-project/smart-camera-hybrid-application/hybrid_app_imx8mp:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
There are two ways to check that the firmware is running:
- Run and observe the output (a pod with the name
example3should be running).
kubectl get pods -A
root@narsil:~# kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
default example3 1/1 Running 0 6m57s
kube-system smarter-cni-wplzn 1/1 Running 3 (141m ago) 4h29m
- Check the Cortex-M Console. If there is any output here, the firmware is running.
Stop the demo
To stop the demo, run the command shown below (the termination process can take a few minutes):
kubectl delete pod example3 --grace-period=0 --force
To make sure the pod was terminated, check the following:
- Go to the Cortex-M Console and check that there are no new outputs:
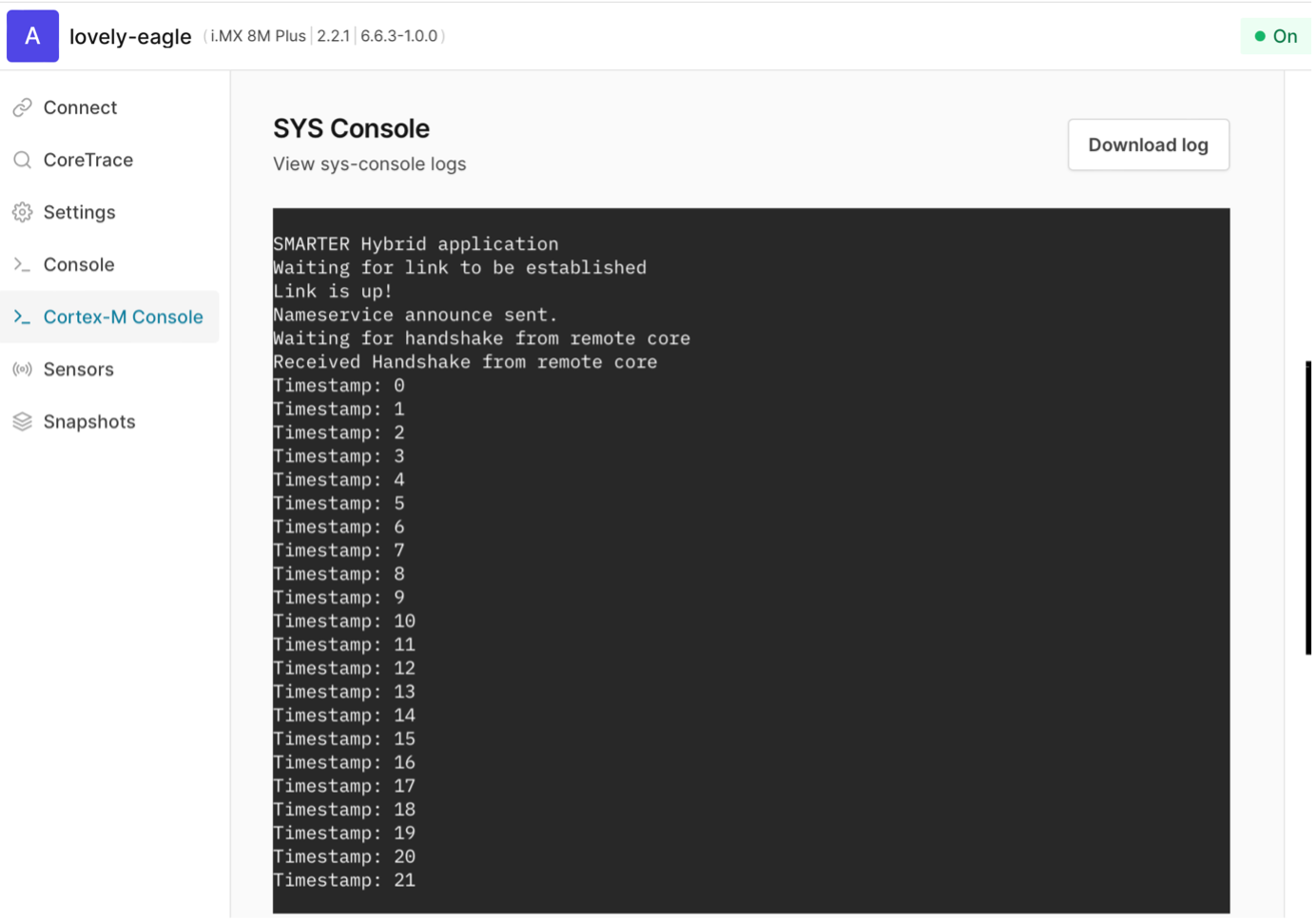 Figure 1. Cortex-M output
Figure 1. Cortex-M output
- Check that the firmware is offline:
cat /sys/class/remoteproc/remoteproc0/state
The output should be as follows:
offline
- Make sure the created pod above was deleted:
kubectl get pods -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system smarter-cni-wplzn 1/1 Running 3 (143m ago) 4h31m
- Make sure all the container resources were deleted. The command below should give no output:
ls /var/lib/hybrid-runtime/
Summary
The hybrid-runtime can be used to improve the experience for systems with multiple IPs on a single SoC. You now know how to use cloud tools such as K3s and containerd to deploy and run workloads on hybrid systems using the hybrid-runtime.
If you have an Arm Linux host, you can run the hello world example by following the instructions in the next section.