Build Zephyr projects with Workbench for Zephyr in VS Code
Introduction
Set up your environment
Build a Zephyr application with Zephyr workbench
Analyze and debug a Zephyr application
Next Steps
Build Zephyr projects with Workbench for Zephyr in VS Code
The benefits of using Workbench for Zephyr Visual Code extension
Getting started with Zephyr RTOS development can be challenging. You often need to install SDKs, set up toolchains, and organize workspace directories by hand. The process is different for each operating system and board vendor, which can make setup confusing and lead to errors.
Workbench for Zephyr is an open-source Visual Studio Code extension that transforms Zephyr RTOS development into a streamlined IDE experience. Created by Ac6 , it automates toolchain setup, project management, and debugging, making Zephyr projects faster to start and easier to scale.
In this Learning Path, you’ll set up Workbench for Zephyr and configure a complete development environment on your computer. By the end, you can create, build, and debug applications for Arm Cortex-M boards using Zephyr RTOS.
Workbench for Zephyr makes it easy to set up your development environment with a single click. It automatically installs all the tools you need, such as Python, CMake, Ninja, and Git. You can import and manage different versions of the Zephyr SDK, choose the right architecture, and quickly initialize West workspaces. The extension lets you create board-specific applications from sample projects, build and flash them to your hardware, and debug your code, all within Visual Studio Code. You also get features like breakpoint debugging and memory usage insights when using a supported hardware probe.
Install dependencies
To get started with Workbench for Zephyr, you need to have Visual Studio Code downloaded, installed, and running on your computer:
Windows
For Windows, you need version 10 or later (64-bit x64), along with administrator privileges for installing runners and drivers.
macOS
On macOS, the Homebrew package manager is required. To install Homebrew, run the following command:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
Linux
To use Workbench for Zephyr on Linux, install a recent 64-bit distribution such as Ubuntu 20.04 or later, Fedora, Clear Linux OS, or Arch Linux. Other distributions can work, but you might need to manually configure some system packages. After installing your operating system, use the Workbench host tools manager to check that all required tools are installed correctly.
Zephyr Workbench supports STM32 development boards (STM32 Discovery, Nucleo series), Nordic Semiconductor boards (nRF52, nRF53, nRF91 series), NXP development boards (FRDM, LPCXpresso series), Espressif boards (ESP32-based boards), and many other Zephyr-supported platforms like Renesas, Silabs or Infineon. You need a development board to try out the code examples.
Install and configure the Zephyr Workbench extension
This section covers installing the Workbench for Zephyr extension and configuring your Arm development environment.
To install the Workbench for Zephyr extension, open Visual Studio Code. In the Activity Bar, select the Extensions icon to open the Extensions view.
You can also use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+X on Windows or Linux, or Cmd+Shift+X on macOS.
In the search box, enter Workbench for Zephyr. Locate the official extension by Ac6 and select Install.
After installation, the Workbench for Zephyr icon appears in the Activity Bar. A welcome screen confirms that the extension is ready to use.
Install the required host tools
In the Workbench for Zephyr panel, select Install Host Tools to automatically install the required dependencies.
This process installs Python 3.x, CMake, the Ninja build system, Git, Device Tree Compiler (DTC), and the West meta-tool.
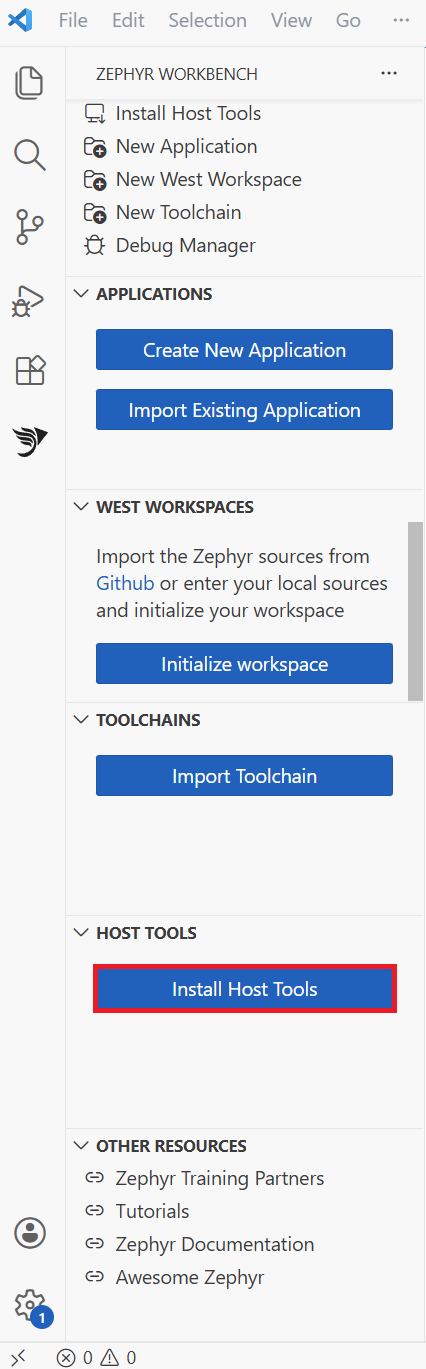 Workbench for Zephyr extension panel
Workbench for Zephyr extension panel
On Windows, you might see permission prompts when Workbench for Zephyr installs or runs tools. Select Allow to continue with the setup.
When the installation completes, select Verify Host Tools to confirm that each required package is installed and up to date. The panel displays the version and status for Python, CMake, Ninja, Git, and Device Tree Compiler. If any tool is missing or out of date, follow the prompts to resolve the issue before continuing.
Import and configure the Zephyr toolchain
To build and debug Zephyr applications for Arm Cortex-M boards, you need to import and configure the Zephyr toolchain using Workbench for Zephyr.
In the Workbench for Zephyr panel, select Import Toolchain. This opens a guided setup panel.
In the Import Toolchain panel, configure the following options to set up your Zephyr toolchain for Arm development:
- Toolchain Family: select Zephyr SDK to use the official Zephyr toolchain.
- SDK Type: select Minimal to install only the essential components needed for development.
- Version: select the Zephyr SDK release you want to use, such as v0.17.0 or v0.17.3.
- Target Architectures: select arm to target Arm-based boards.
These settings ensure your environment is optimized for Arm Cortex-M development. After configuring these options, continue with the import process to download and install the selected SDK.
Next, specify the directory where you want to install the SDK. Select Import to start the download and installation process. When the import completes, the panel displays a confirmation that the toolchain is ready.
If you see errors during import, check your internet connection and confirm you have at least 2 GB of free disk space. For more troubleshooting tips, review the extension’s documentation or check the Visual Studio Code output panel.
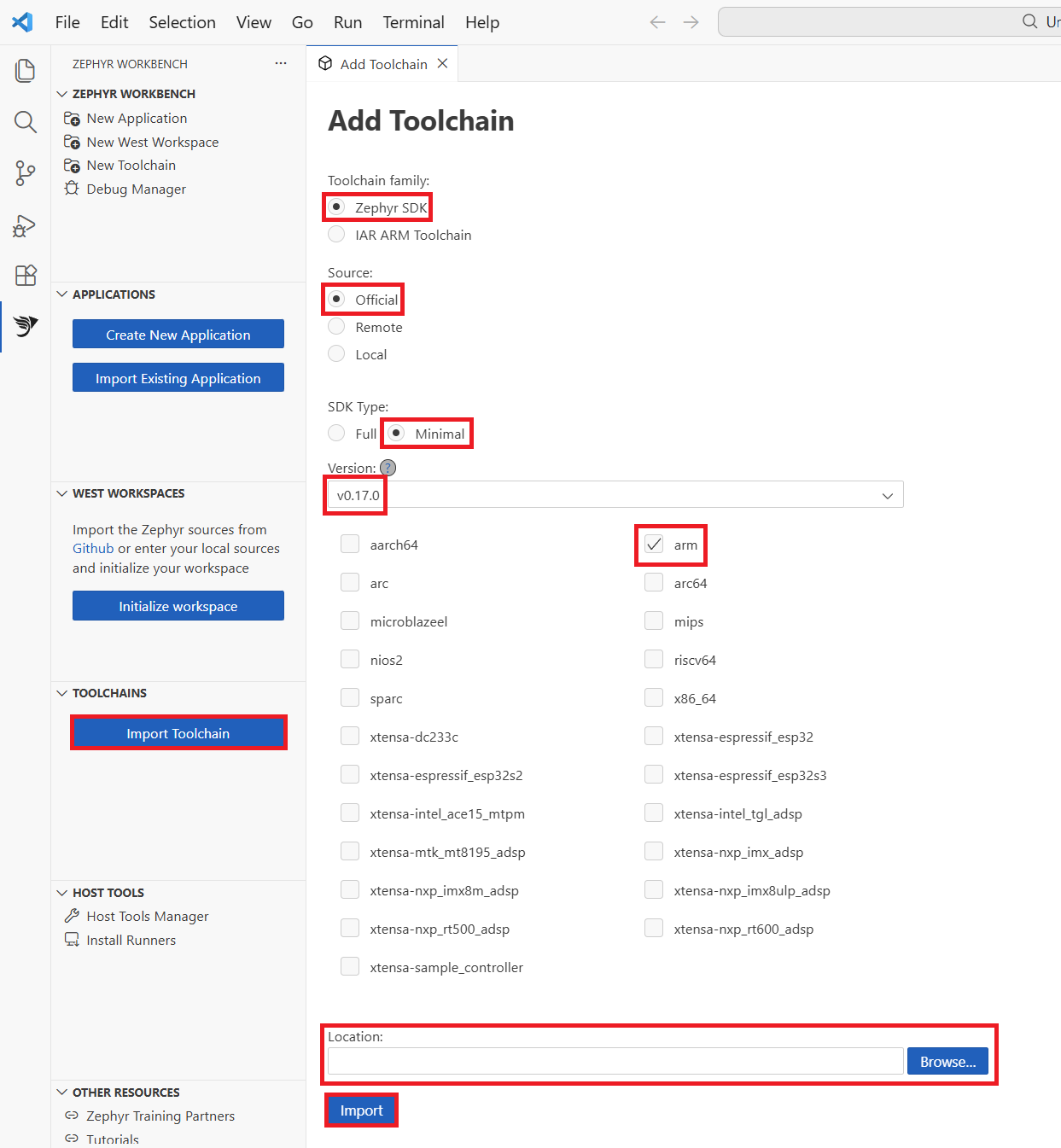 Workbench for Zephyr Import Toolchain panel
Workbench for Zephyr Import Toolchain panel
Initialize the Zephyr project workspace
Zephyr uses a Git-based workspace manager called West to organize its source code, modules, and samples. Use Workbench for Zephyr to initialize your first West workspace.
In the Workbench for Zephyr panel, select Initialize Workspace to set up your project environment. Configure the workspace settings by selecting Minimal from template for the source location and using the default path https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/zephyr.
Choose a target-specific template (such as STM32 or NXP) and select your Zephyr version (such as v4.3.0… your version may vary a bit). Specify the directory for your workspace, keeping in mind that initialization takes approximately 10 minutes to complete.
Select Import to create and update the workspace.
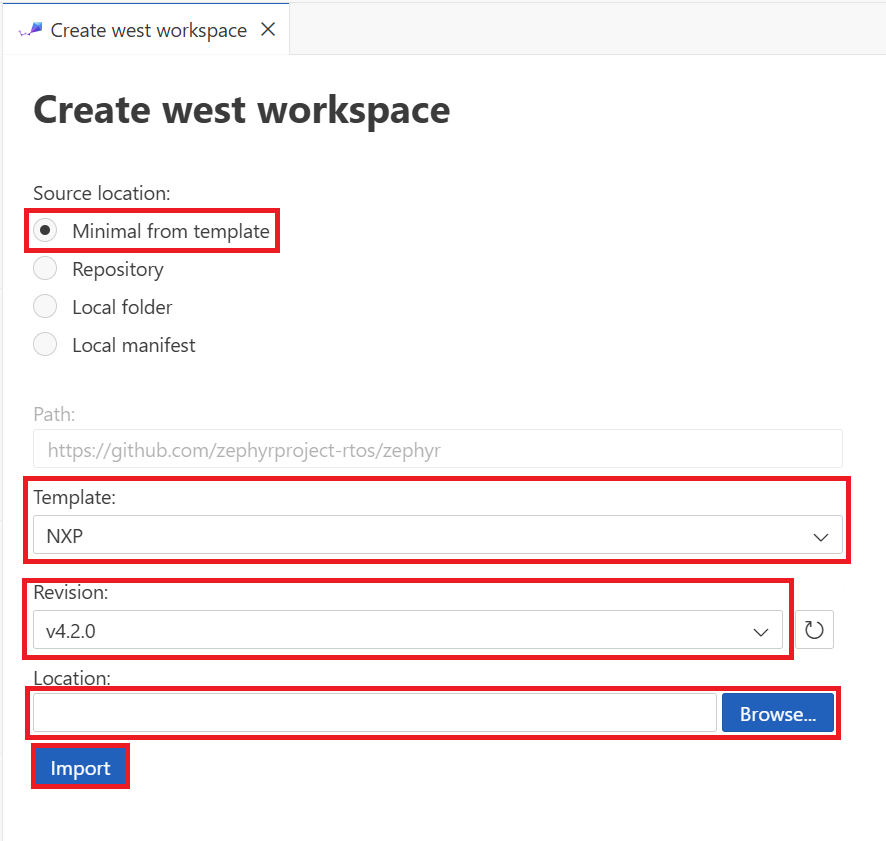 Workbench for Zephyr Initialize Workspace panel in Visual Studio Code.
Workbench for Zephyr Initialize Workspace panel in Visual Studio Code.
The workspace initialization downloads the Zephyr source code and dependencies. This process can take several minutes depending on your internet connection speed.
Verify setup
Test your setup by confirming that the Workbench for Zephyr panel shows all components as installed successfully. Verify the host tools are installed, the SDK is imported and detected, and the West workspace is initialized. Ensure no error messages appear in the VS Code output panel.
You’re now ready to create and build your first Zephyr application targeting an Arm Cortex-M board.