Edge AI on Arm: PyTorch and ExecuTorch rock-paper-scissors
Introduction
Set up your environment
Train and Test the rock-paper-scissors Model
Run the model on Corstone-320 FVP
Next Steps
Edge AI on Arm: PyTorch and ExecuTorch rock-paper-scissors
Set up your environment for Tiny rock-paper-scissors on Arm
This Learning Path is a direct follow-up to Introduction to TinyML on Arm using PyTorch and ExecuTorch . While the previous Learning Path introduced the core concepts and toolchain, this one puts that knowledge into practice with a small, real-world example. You move from a simple Feedforward Neural Network to a practical computer vision task: a tiny rock-paper-scissors game that runs efficiently on Arm-based edge devices.
You will train a lightweight CNN to classify images of the letters R, P, and S as “rock,” “paper,” or “scissors.” The script uses a synthetic data renderer to create a large dataset of these images with various transformations and noise, eliminating the need for a massive real-world dataset.
What is a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)?
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of deep neural network primarily used for analyzing visual imagery. Unlike traditional neural networks, CNNs are designed to process pixel data by using a mathematical operation called convolution. This allows them to automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of features from input images, from low-level features like edges and textures to high-level features like shapes and objects.
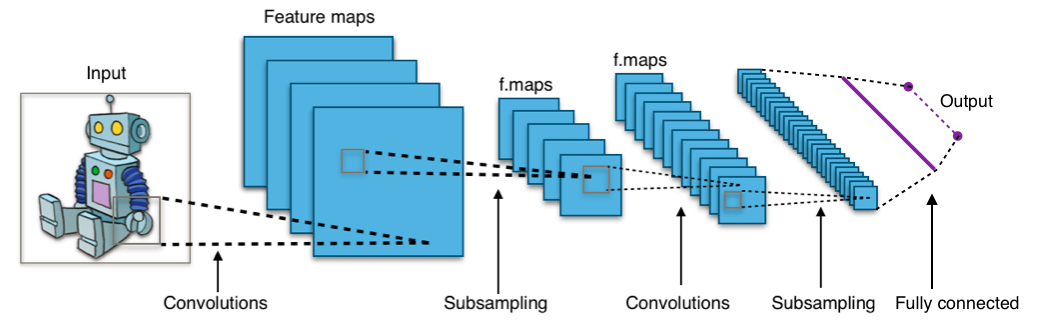
Typical CNN architecture by Aphex34, licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 .
Common CNN applications include:
- Image classification: identify the main object in an image, such as classifying a photo as a cat or dog
- Object detection: locate specific objects in an image and draw bounding boxes
- Facial recognition: identify or verify individuals based on facial features
For the rock-paper-scissors game, you use a tiny CNN to classify the letters R, P, and S as the corresponding hand gestures.
Environment setup
To get started, complete the first three sections of
Introduction to TinyML on Arm using PyTorch and ExecuTorch
. This setup prepares your development environment and installs the required tools. Return here after running the ./examples/arm/run.sh script in the ExecuTorch repository.
If you just completed the earlier Learning Path, your virtual environment should still be active. If not, activate it:
source $HOME/executorch-venv/bin/activate
The prompt of your terminal now has (executorch-venv) as a prefix to indicate the virtual environment is active.
Install Python dependencies:
pip install numpy pillow torch
You’re now ready to create the model.