Create and train a PyTorch model for digit classification using the MNIST dataset
Introduction
Prepare a PyTorch Development Environment
Create a PyTorch model for MNIST
About PyTorch Model Training
Perform Training and Save the Model
Deploy the Model for Inference
Learn about Inference on Android
Create an Android Application
Prepare the Test Data
Run the Application
Optimizing Neural Network Models in PyTorch
Create an optimized PyTorch model for MNIST
Run optimization
Update the Android application
Next Steps
Create and train a PyTorch model for digit classification using the MNIST dataset
Introduction
Prepare a PyTorch Development Environment
Create a PyTorch model for MNIST
About PyTorch Model Training
Perform Training and Save the Model
Deploy the Model for Inference
Learn about Inference on Android
Create an Android Application
Prepare the Test Data
Run the Application
Optimizing Neural Network Models in PyTorch
Create an optimized PyTorch model for MNIST
Run optimization
Update the Android application
Next Steps
You can now use the optimized model in the Android application you developed earlier.
Start by modifying the activity_main.xml by adding a CheckBox to use the optimized model:
<!-- CheckBox to use optimised model -->
<CheckBox
android:id="@+id/checkboxOptimizedModel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Use optimised model?"
android:textSize="16sp"/>
Copy the optimized model to the assets folder in the Android project.
Replace the code in MainActivity.kt Kotlin file with the following code:
package com.arm.armpytorchmnistinference
import android.graphics.Bitmap
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.CheckBox
import android.widget.ImageView
import android.widget.TextView
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import org.pytorch.IValue
import org.pytorch.Module
import org.pytorch.Tensor
import java.io.File
import java.io.FileOutputStream
import java.io.IOException
import java.io.InputStream
import kotlin.random.Random
import kotlin.system.measureNanoTime
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var imageView: ImageView
private lateinit var trueLabel: TextView
private lateinit var selectImageButton: Button
private lateinit var runInferenceButton: Button
private lateinit var predictedLabel: TextView
private lateinit var inferenceTime: TextView
private lateinit var model: Module
private lateinit var checkboxOptimizedModel: CheckBox // Add CheckBox for switching models
private var currentBitmap: Bitmap? = null
private var currentTrueLabel: Int? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// Initialize UI elements
imageView = findViewById(R.id.imageView)
trueLabel = findViewById(R.id.trueLabel)
selectImageButton = findViewById(R.id.selectImageButton)
runInferenceButton = findViewById(R.id.runInferenceButton)
predictedLabel = findViewById(R.id.predictedLabel)
inferenceTime = findViewById(R.id.inferenceTime)
checkboxOptimizedModel = findViewById(R.id.checkboxOptimizedModel)
// Initially load the appropriate model based on the CheckBox state
loadModel()
// Set up button click listener for selecting random image
selectImageButton.setOnClickListener {
selectRandomImageFromAssets()
}
// Set up button click listener for running inference
runInferenceButton.setOnClickListener {
currentBitmap?.let { bitmap ->
runInference(bitmap)
}
}
// Set up listener for checkbox to switch models dynamically
checkboxOptimizedModel.setOnCheckedChangeListener { _, _ ->
loadModel() // Reload the model when checkbox state changes
}
}
// Load the appropriate model based on the CheckBox state
private fun loadModel() {
try {
model = if (checkboxOptimizedModel.isChecked) {
// Load the optimized model
Module.load(assetFilePath("optimized_model.ptl"))
} else {
// Load the original model
Module.load(assetFilePath("model.pth"))
}
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
trueLabel.text = "Error loading model"
}
}
private fun selectRandomImageFromAssets() {
try {
// Get list of files in the mnist_bitmaps folder
val assetManager = assets
val files = assetManager.list("mnist_bitmaps") ?: arrayOf()
if (files.isEmpty()) {
trueLabel.text = "No images found in assets/mnist_bitmaps"
return
}
// Select a random file from the list
val randomFile = files[Random.nextInt(files.size)]
val inputStream: InputStream = assetManager.open("mnist_bitmaps/$randomFile")
val bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(inputStream)
// Extract the true label from the filename (e.g., 07_00.png -> true label is 7)
currentTrueLabel = randomFile.split("_")[0].toInt()
// Display the image and its true label
imageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap)
trueLabel.text = "True Label: $currentTrueLabel"
// Set the current bitmap for inference
currentBitmap = bitmap
} catch (e: IOException) {
e.printStackTrace()
trueLabel.text = "Error loading image from assets"
}
}
// Method to convert a grayscale bitmap to a float array and create a tensor with shape [1, 1, 28, 28]
private fun createTensorFromBitmap(bitmap: Bitmap): Tensor {
// Ensure the bitmap is in the correct format (grayscale) and dimensions [28, 28]
if (bitmap.width != 28 || bitmap.height != 28) {
throw IllegalArgumentException("Expected bitmap of size [28, 28], but got [${bitmap.width}, ${bitmap.height}]")
}
// Convert the grayscale bitmap to a float array
val width = bitmap.width
val height = bitmap.height
val floatArray = FloatArray(width * height)
val pixels = IntArray(width * height)
bitmap.getPixels(pixels, 0, width, 0, 0, width, height)
for (i in pixels.indices) {
// Normalize pixel values to [0, 1] range, assuming the grayscale image stores values in the R channel
floatArray[i] = (pixels[i] and 0xFF) / 255.0f
}
// Create a tensor with shape [1, 1, 28, 28] (batch size, channels, height, width)
return Tensor.fromBlob(floatArray, longArrayOf(1, 1, height.toLong(), width.toLong()))
}
private fun runInference(bitmap: Bitmap, N: Int = 100) {
// Convert bitmap to a float array and create a tensor with shape [1, 1, 28, 28]
val inputTensor = createTensorFromBitmap(bitmap)
// Run inference and measure time
val inferenceTimeMicros = measureTimeMicros {
var maxIndex = 0
var scores: FloatArray = FloatArray(10)
// Run inference N times
for (i in 1..N) {
// Forward pass through the model
val outputTensor = model.forward(IValue.from(inputTensor)).toTensor()
scores = outputTensor.dataAsFloatArray
}
// Get the index of the class with the highest score
maxIndex = scores.indices.maxByOrNull { scores[it] } ?: -1
predictedLabel.text = "Predicted Label: $maxIndex"
}
// Update inference time TextView in microseconds
inferenceTime.text = "Inference Time: $inferenceTimeMicros µs"
}
// Method to measure execution time in microseconds
private inline fun measureTimeMicros(block: () -> Unit): Long {
val time = measureNanoTime(block)
return time / 1000 // Convert nanoseconds to microseconds
}
// Helper function to get the file path from assets
private fun assetFilePath(assetName: String): String {
val file = File(filesDir, assetName)
assets.open(assetName).use { inputStream ->
FileOutputStream(file).use { outputStream ->
val buffer = ByteArray(4 * 1024)
var read: Int
while (inputStream.read(buffer).also { read = it } != -1) {
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, read)
}
outputStream.flush()
}
}
return file.absolutePath
}
}
The updated version of the Android application includes modifications to the Android Activity source code to dynamically load the model based on the state of the CheckBox.
When the CheckBox is selected, the app loads the optimized model, which is quantized and fused for improved performance.
If the CheckBox is not selected, the app loads the original model.
After the model is loaded, the inference is run. To better estimate the execution time, the runInference() method executes the inference 100 times in a loop. This provides a more reliable measure of the average inference time by smoothing out any inconsistencies from single executions.
The results for a run on a physical device are shown below. These results indicate that, on average, the optimized model reduced the inference time to about 65% of the original model’s execution time, which demonstrates a significant improvement in performance.
This optimization showcases the benefits of quantization and layer fusion for mobile inference, and there is further potential for enhancement by enabling hardware acceleration on supported devices.
This would allow the model to take full advantage of the device’s computational capabilities, potentially further reducing the inference time.
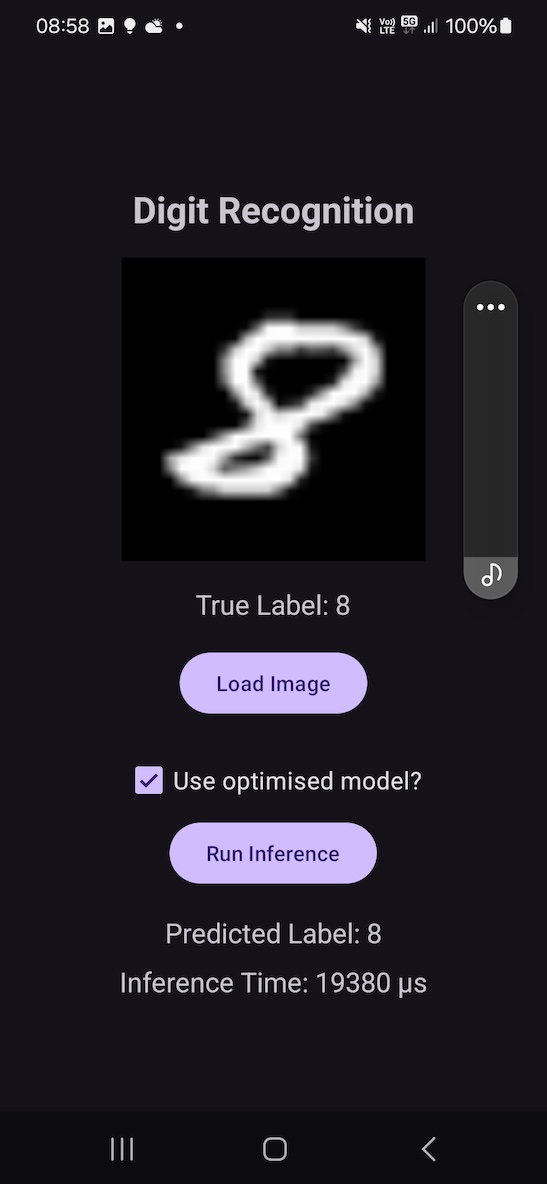 Figure 9.
Figure 9.
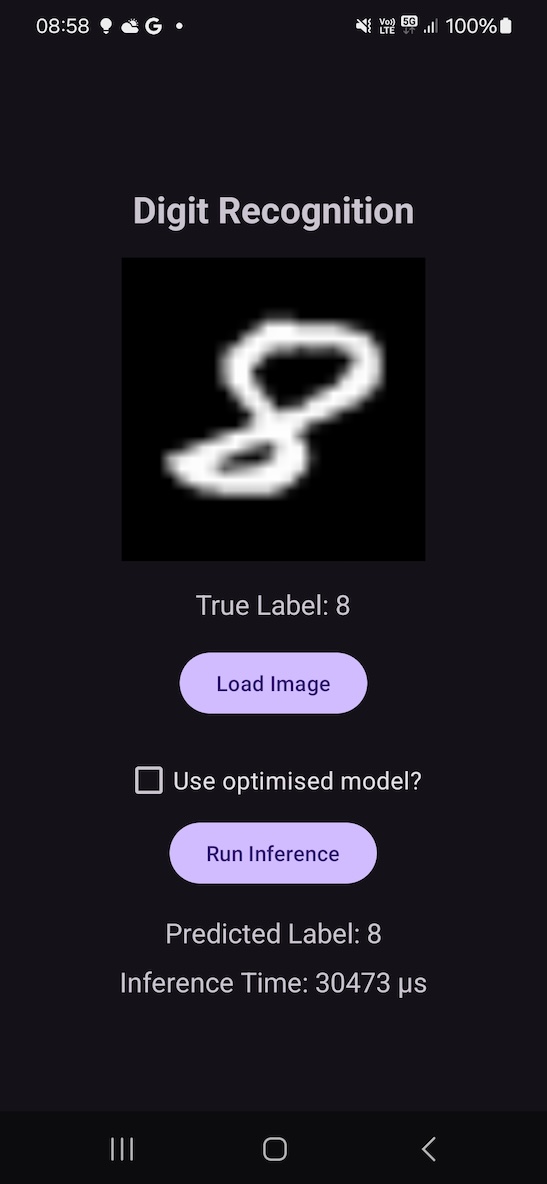 Figure 10.
Figure 10.
What have you learned?
You have successfully optimized a neural network model for mobile inference using quantization and layer fusion.
Quantization and layer fusion removes unnecessary elements such as dropout layers during inference.
By running multiple iterations of the inference process, you learned that the optimized model significantly reduced the average inference time to around 65% of the original time.
You also learned that there is potential for further performance improvements by leveraging hardware acceleration.