Build multi-architecture container images with GitHub Arm-hosted runners
Introduction
Build options for multi-architecture container images
Arm-hosted runners for public repositories
Create a new Arm-hosted runner for private repositories
Run GitHub Actions jobs on the Arm-hosted runner
Next Steps
Build multi-architecture container images with GitHub Arm-hosted runners
Use GitHub Actions
You can use GitHub Actions to build multi-architecture images by creating a workflow file and using Arm-hosted runners.
Create a new GitHub repository
To get started, create a new GitHub repository in your GitHub account.
Log in to your GitHub account using your browser. Select the
New Button
to create a new repository. Give the repository a name. Click Create Repository.
If you need more detailed instructions, there are numerous tutorials on how to create a repository or refer to the GitHub documentation .
Set up secrets
The container images created by GitHub Actions are stored on Docker Hub.
To run GitHub Actions, you need your Docker Hub username and a Personal Access Token (PAT). This enables you to automate the login to your Docker Hub account.
To save your secrets, click on the Settings tab in your new GitHub repository. Expand the Secrets and variables on the left side and click Actions.
Add two secrets using the New repository secret button:
DOCKER_USERwith your Docker ID.DOCKER_PATwith your Personal Access Token.
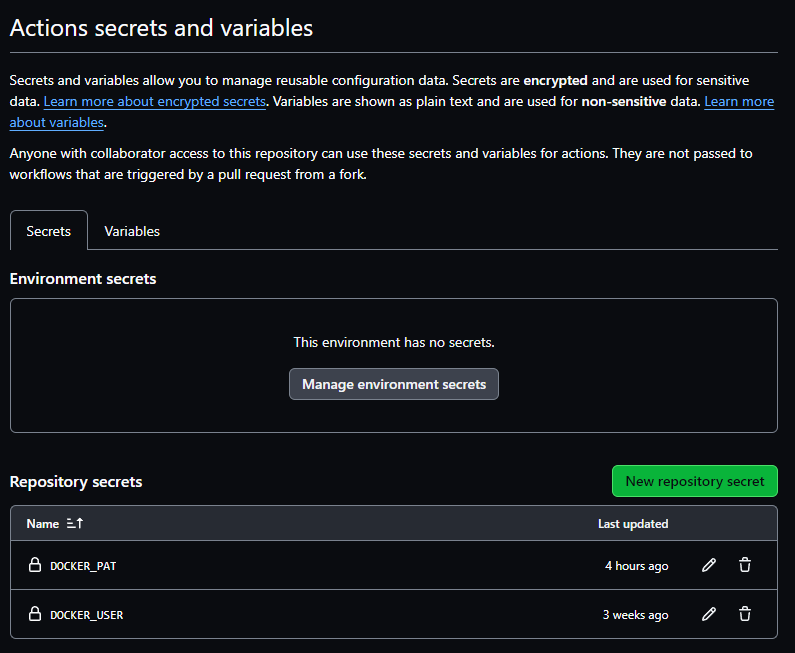
You have stored the secrets that allow you to login to Docker Hub and save container images.
Add files to the repository
To use GitHub Actions to build a container image and store it on Docker Hub, you need to add two files to your repository.
First, create a file named Dockerfile with the contents below at the top of the repository.
FROM ubuntu:latest
CMD echo -n "Architecture is " && uname -m
You can do this in the browser using the Add file button to create a new file, or upload the file from your computer. You can also use git from the command line.
Next, add the image-build.yml file with the contents below to the .github/workflows directory in your repository:
name: image-build
on:
workflow_dispatch:
env:
USER: ${{secrets.DOCKER_USER}}
jobs:
docker_build:
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
matrix:
include:
- os: ubuntu-latest
arch: amd64
- os: ubuntu-22.04-arm
arch: arm64
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Log in to Docker Hub
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
username: ${{env.USER}}
password: ${{secrets.DOCKER_PAT}}
- name: Build and push
run: |
docker build --tag ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname:${{matrix.arch}} .
docker push ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname:${{matrix.arch}}
docker_manifest:
needs: docker_build
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Log in to Docker Hub
uses: docker/login-action@v3
with:
username: ${{env.USER}}
password: ${{secrets.DOCKER_PAT}}
- name: Create and push manifest
run: |
docker manifest create ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname:amd64 ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname:arm64
docker manifest push ${{env.USER}}/docker-uname
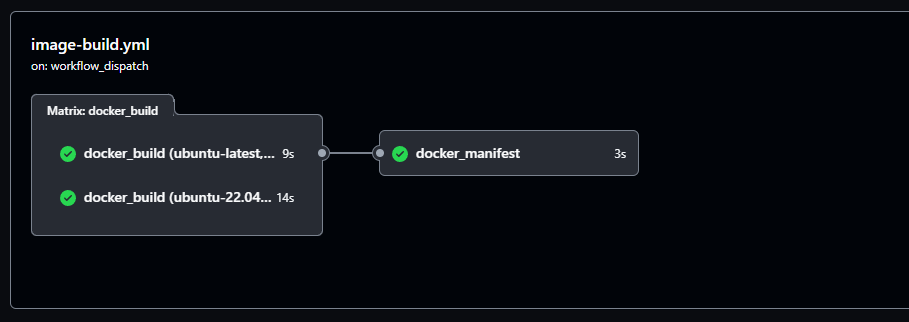
The workflow file uses a job matrix to run two jobs in parallel. One job runs docker build on the new Arm-hosted runner. The second job runs docker build on a standard runner with the amd64 architecture. When both jobs are done, the final job uses docker manifest to create the multi-architecture image.
With the two files and the two secrets in your repository, you are ready to run the action.
Run the GitHub Action
To run the action, navigate to the Actions tab in your repository.
Select the image-build on the left.
Use the Run workflow drop-down on the right-hand side to click Run workflow.
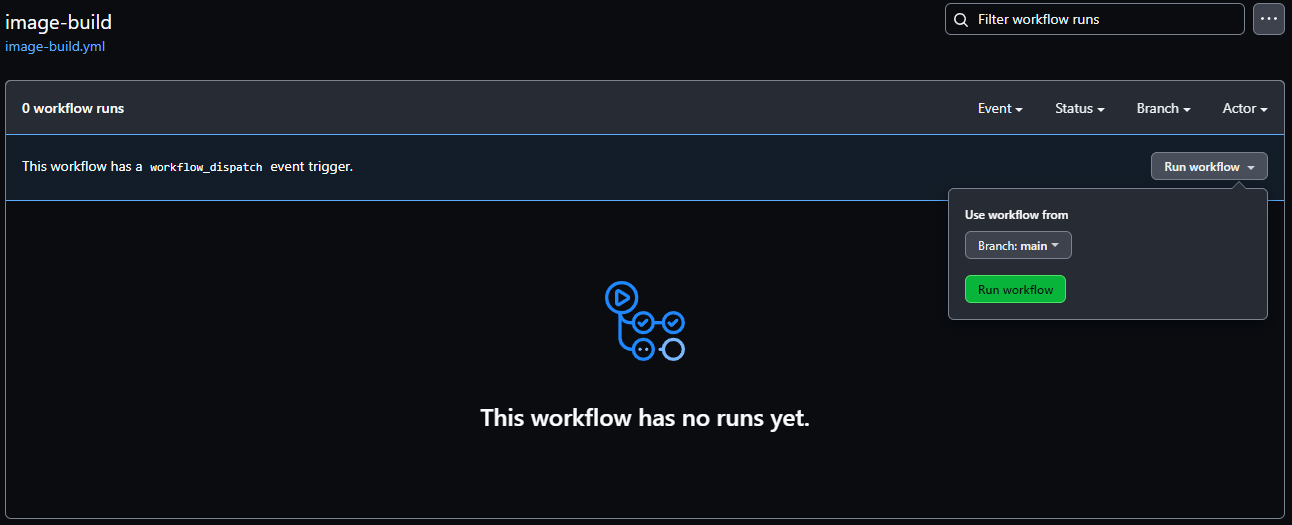
This triggers the image-build workflow to start, performing the following steps:
- Checkout the repository.
- Log in to Docker Hub.
- Run the
docker buildcommand to build an image from theDockerfileand push the image to your Docker Hub account.
This flow is executed twice, once on the Arm-hosted runner to produce the arm64 image, and once on the standard runner to produce the amd64 image.
When the workflow completes, the new image is available in your Docker Hub account.
You can use the Actions tab in your repository to see if the workflow runs, click on each one to review the commands, and check errors.
Automate the build
Instead of manually triggering the build, you can modify the image-build.yml to automatically run the workflow when changes are made to the Dockerfile. Add the push: line as shown below to automatically run the action when a push is made to any branch in the repository.
name: image-build
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
If you make a change to your Dockerfile and push it to the repository, the workflow automatically runs.
You can now use GitHub Actions to build multi-architecture images without using QEMU instruction emulation or using a self-hosted runner on a Arm server.