There are many ways to check if container images are built for multiple architectures and if they support the Arm architecture.
Some of the common ways are provided below.
Look at the image information in the container registry
One way to check images is to use a browser and inspect the image in the registry.
For example, on Docker Hub, the architectures are printed.
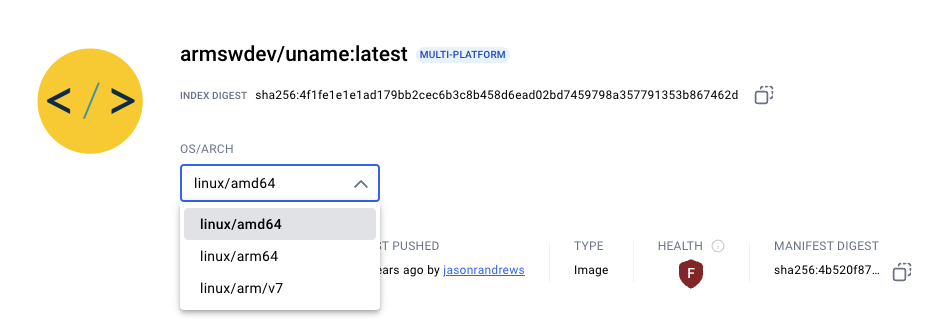
AWS ECR Public registry also prints the architectures.
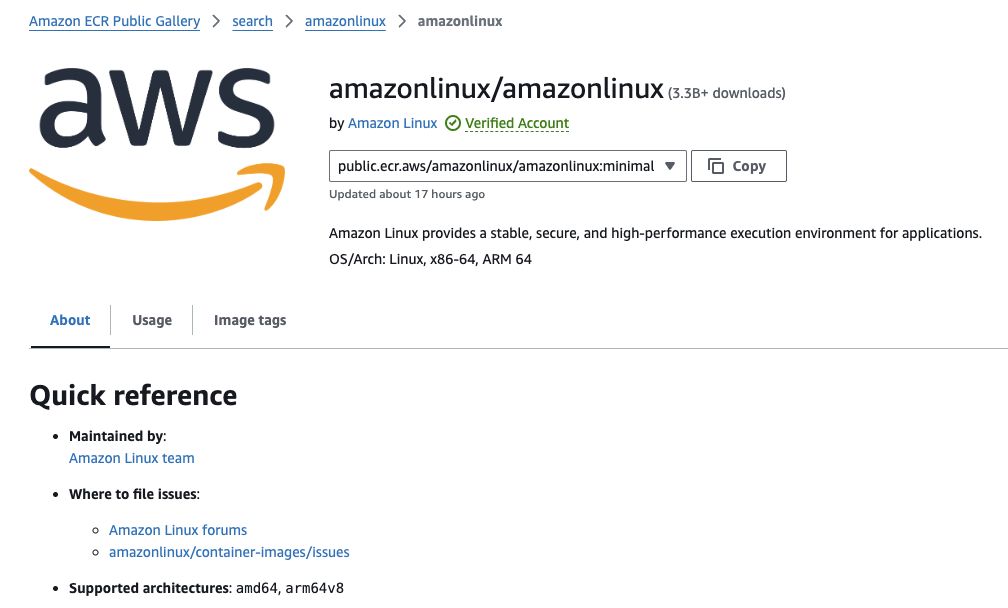
If you see arm64, ARM64, or arm64v8 on the list, then the image supports Arm.
Not all container registries have a web view showing architecture support. Additional ways to find the information are provided below.
Use Docker CLI commands
Inspect the image manifest
docker manifest inspect armswdev/uname:latest
Look for “arm64” in the output.
You can use grep to check for arm64:
docker manifest inspect armswdev/uname:latest | grep arm64
The output confirms arm64 support:
"architecture": "arm64",
Use Docker buildx to inspect the image
docker buildx imagetools inspect --format '{{json (index .Image "linux/arm64")}}' armswdev/uname:latest
If this command returns JSON data, the image supports Arm.
If the image does not support Arm an error is printed:
ERROR: template: :1:8: executing "" at <index .Image "linux/arm64">: error calling index: can't index item of type v1.Image
Inspect image metadata
The image inspect command works on local images so use docker pull to get the image.
docker image inspect armswdev/uname:latest
Look for “Architecture”: “arm64” in the output.
Use a formatted inspect command
For concise output print only the architecture:
docker inspect -f '{{.Architecture}}' armswdev/uname:latest
This will directly output the architecture.
arm64
Can I use a script to check if a container image supports the Arm architecture?
You can run a script to check container images for arm64 support.
The script performs the following tasks:
- Get a token for the registry
- Read the image manifest
- Check the manifest for architecture support
Make sure Python3 is installed on your computer.
Use a text editor to copy the Python code below to a file named check-image.py.
import requests
import sys
import os
import argparse
from typing import List, Dict, Tuple
# Target architectures to check
TARGET_ARCHITECTURES = {'amd64', 'arm64'}
TIMEOUT_SECONDS = 10
def get_auth_token(repository: str) -> str:
"""Get Docker Hub authentication token."""
url = "https://auth.docker.io/token"
params = {
"service": "registry.docker.io",
"scope": f"repository:{repository}:pull"
}
try:
response = requests.get(url, params=params, timeout=TIMEOUT_SECONDS)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()['token']
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Failed to get auth token: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
def get_manifest(repository: str, tag: str, token: str) -> Dict:
"""Fetch manifest for specified image."""
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/vnd.docker.distribution.manifest.list.v2+json',
'Authorization': f'Bearer {token}'
}
url = f"https://registry-1.docker.io/v2/{repository}/manifests/{tag}"
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=TIMEOUT_SECONDS)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Failed to get manifest: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
def check_architectures(manifest: Dict) -> List[str]:
"""Check available architectures in the manifest."""
if manifest.get('manifests'):
archs = [m['platform']['architecture'] for m in manifest['manifests']]
return archs
else:
return []
def parse_image_spec(image: str) -> Tuple[str, str]:
"""Parse image specification into repository and tag."""
if ':' in image:
repository, tag = image.split(':', 1)
else:
repository, tag = image, 'latest'
if '/' not in repository:
repository = f'library/{repository}'
return repository.lower(), tag
def parse_args():
"""Parse command line arguments."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Check Docker image architectures')
parser.add_argument('image', help='Docker image name (format: name:tag)')
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = parse_args()
repository, tag = parse_image_spec(args.image)
token = get_auth_token(repository)
manifest = get_manifest(repository, tag, token)
architectures = check_architectures(manifest)
if not architectures:
print(f"No architectures found for {args.image}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
available_targets = TARGET_ARCHITECTURES.intersection(architectures)
missing_targets = TARGET_ARCHITECTURES - set(architectures)
if not missing_targets:
print(f"✓ Image {args.image} supports all required architectures")
else:
print(f"✗ Image {args.image} is missing architectures: {', '.join(missing_targets)}")
print(f"Available architectures: {', '.join(architectures)}")
The script queries Docker Hub. If needed, you can change the registry and the architecture list to meet your needs.
Run the script asking about Alpine Linux:
python3 ./check-image.py alpine:3.21.0
The output indicates that the image supports both arm64 and amd64:
✓ Image alpine:3.21.0 supports all required architectures
You can now identify if container images are built for multi-architecture support, including the Arm architecture.