Build multi-architecture container images with Docker Build Cloud
Introduction
Setup and build images with Docker Build Cloud
Use GitHub Actions with Docker Build Cloud
Next Steps
Build multi-architecture container images with Docker Build Cloud
Methods to build multi-architecture container images
Building multi-architecture container images is challenging for complex projects.
There are two common ways to build multi-architecture images, and both are explained in Learn how to use Docker .
The first method is to use instruction emulation. You can learn about this method in Build multi-architecture images with Docker buildx . The drawback of emulation is slow performance, especially for complex builds which involve tasks such as compiling large C++ applications.
The second method is to use multiple machines, one for each architecture, and then join the images to make a multi-architecture image using Docker manifest. You can learn about this method in Use Docker manifest to create multi-architecture images . The drawback of using a manifest is complexity as multiple machines are required to execute a multi-step process.
Docker Build Cloud provides a way to create multi-architecture images with higher performance and lower complexity compared to the two methods described above. With Docker Build Cloud you don’t need to worry about extra hardware, instruction emulation, or joining images together manually. Docker Build Cloud is a cloud service that takes care of everything, transparently.
Before you begin
You can use any computer running Docker to complete this Learning Path.
To confirm that Docker is installed, run the following command:
docker run hello-world
If Docker is installed and working, you will see the following message:
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
<extra output omitted>
If you do not see the message above, go to Installing Docker and follow the instructions to complete the installation.
In addition to having Docker installed, you will also need a Docker Hub account.
You will need a credit card to use Docker Build Cloud (you don’t need to pay anything to try it, but you do need to enter your credit card details).
You will need a Docker subscription for Docker Team or Docker Business to build multi-architecture images. Visit Docker Build Cloud pricing for more information.
You can build single architecture images for free using a Docker Personal account and the included monthly minutes.
It may help to review the first two sections of Learn how to use Docker so that you are familiar with the basics before trying Docker Build Cloud.
Create a Cloud Builder
To get started, log in to Docker Build Cloud at https://build.docker.com using your Docker ID and password.
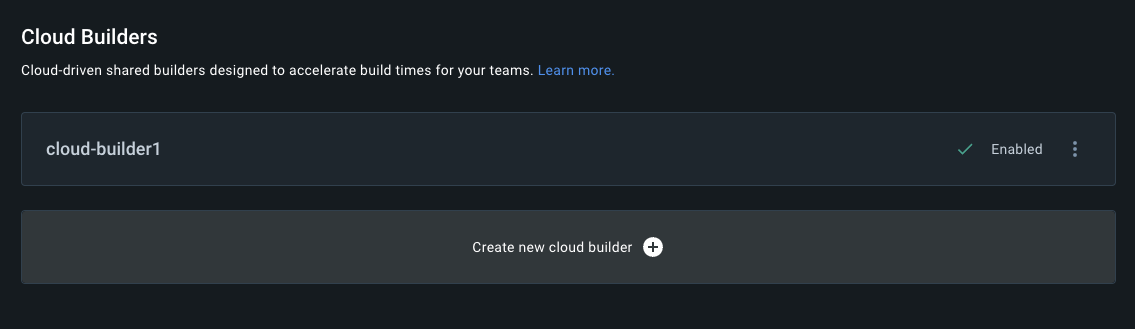
Click on Create new cloud builder. The button is shown in the screen shot below.
Enter a name for the builder. For example, cloud-builder1.
It will take a few minutes to create the new builder but it will appear on your dashboard with a green check mark next to Enabled as shown below:
Add the builder on your local machine
Open a terminal on your local computer and log in with your Docker ID and password (or Personal Access Token (PAT)).
docker login
Create the connection to the cloud builder on your local machine. Replace username with your Docker ID or the Organization for your Docker subscription.
docker buildx create --use --driver cloud username/cloud-builder1
If you are using Docker Engine on Linux (not Docker Desktop), you will get the following error:
ERROR: failed to find driver "cloud"
If you see this error, follow the steps in the next section.
If you don’t see the error, you are likely using Docker Desktop and you can continue to the Display the new cloud builder section.
Additional steps for Docker Engine (Linux)
To use Docker Build Cloud, you need a version of buildx that includes cloud builder support.
Updating buildx requires the jq command. Install it using your package manager:
sudo apt-get install jq -y
Use a text editor to copy the code below into a file named update-buildx.sh.
The architecture is set to arm64 but you can change it to match your system as needed.
#!/bin/bash
# Get download link for latest buildx binary. Set $ARCH to the CPU architecture (e.g. amd64, arm64)
ARCH=arm64
BUILDX_URL=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/docker/actions-toolkit/main/.github/buildx-lab-releases.json | jq -r ".latest.assets[] | select(endswith(\"linux-$ARCH\"))")
# Download docker buildx with Hyrdobuild support
mkdir -vp ~/.docker/cli-plugins/
curl --silent -L --output ~/.docker/cli-plugins/docker-buildx $BUILDX_URL
chmod a+x ~/.docker/cli-plugins/docker-buildx
The script comes from the Docker documentation on using Docker Build Cloud for CI. Refer to Use Docker Build Cloud in CI for more details.
Run the script:
bash -x ./update-buildx.sh
Try again to create the cloud builder. Replace username with your Docker ID or Organization.
docker buildx create --use --driver cloud username/cloud-builder1
Display the new cloud builder
Confirm the builder is available using the ls command:
docker buildx ls
You will see a new builder listed:
NAME/NODE DRIVER/ENDPOINT STATUS BUILDKIT PLATFORMS
cloud-username-cloud-builder1 * cloud
linux-arm64 cloud://username/cloud-builder1_linux-arm64 running v0.12.5 linux/arm64*
linux-amd64 cloud://username/cloud-builder1_linux-amd64 running v0.12.5 linux/amd64*, linux/amd64/v2, linux/amd64/v3, linux/amd64/v4
Your cloud builder is now ready to use.
Build a Docker image from a Dockerfile
Use a text editor to create a new file named Dockerfile with the following contents:
FROM ubuntu:latest
CMD echo -n "Architecture is " && uname -m
Build the image with the new cloud builder (substituting your Docker ID or Organization for username):
docker buildx build --builder cloud-username-cloud-builder1 --tag cloud-build-test .
When the build completes, you will have an image for the architecture of your local computer.
docker images
The output shows the following image:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
cloud-build-test latest ec5a0a70e7d3 2 weeks ago 69.2MB
hello-world latest ee301c921b8a 9 months ago 9.14kB
The commands below are for the Arm architecture. If you have another architecture, you can change the --platform argument to match your architecture.
Run the new image and it will print the architecture of your local machine.
docker run --rm cloud-build-test
The output is:
Architecture is aarch64
The image created is for the architecture of your computer.
You can build an image for a different architecture using the cloud builder.
Replace username with your Docker ID or Organization in the commands as needed.
For example:
docker buildx build --platform linux/amd64 --builder cloud-username-cloud-builder1 --tag cloud-build-test .
The new image replaces the one on your local computer.
To run it, specify the architecture it was built for:
docker run --platform linux/amd64 --rm cloud-build-test
The output is now:
Architecture is x86_64
If you get an error and you are using Docker Engine on Linux, you may need to enable instruction emulation.
sudo apt-get install qemu-user-static -y
Multi-architecture build
To build a multi-architecture image with a single command, you need to specify a list of architectures you want the image to support.
For example:
docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64,linux/arm/v7 --builder cloud-username-cloud-builder1 --tag cloud-build-test .
Multi-architecture images cannot be pulled automatically so the above command will generate an error:
ERROR: cloud pull for multi-node builds currently not supported
To build the multi-architecture image use --push to save it to your Docker Hub account. Make sure to add your Docker ID to the tag so that it can be pushed to your Docker Hub account.
docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64,linux/arm/v7 --builder cloud-username-cloud-builder1 --tag username/cloud-build-test --push .
You now have a multi-architecture image (two different Arm architectures) in your Docker Hub account which can be pulled and run on any computer, which is one of the architectures specified during the build.
To build for different architectures you can change the list specified with --platform:
docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64,linux/amd64 --builder cloud-username-cloud-builder1 --tag username/cloud-build-test --push .
The above command will fail if you do not have a Docker Team or Docker Business subscription.
If you have Docker Personal or Docker Pro the error is:
ERROR: failed to solve: FailedPrecondition: build cannot proceed concurrent build limit of 1 reached
If you are part of an organization with a Docker subscription, the command will succeed.
Using a cloud service simplifies multi-architecture builds and shortens build time for complex images.