OpenVSCode Server
About this Install Guide
| Reading time: | 30 min |
| Last updated: | 30 Jan 2026 |
| Reading time: |
| 30 min |
| Last updated: |
| 30 Jan 2026 |
This guide shows you how to install and use the tool with the most common configuration. For advanced options and complete reference information, see the official documentation. Some install guides also include optional next steps to help you explore related workflows or integrations.
OpenVSCode Server is a version of VS Code which runs on any computer and can be accessed using a browser. The project was initiated by Gitpod and is available on GitHub
OpenVSCode Server supports the Arm architecture and is useful for developing on a remote Arm machine. It can be used on cloud instances, without requiring a Linux desktop to be installed. It’s also useful when developing on a local Arm machine with a Linux subsystem, such as Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), ChromeOS with Linux enabled, or Multipass.
What do I need before installing OpenVSCode Server?
Follow the instructions below to install OpenVSCode Server natively on an Arm Linux machine.
Confirm you are using an Arm machine by running:
uname -m
The output should be:
aarch64
If you see a different result, you are not using an Arm computer running 64-bit Linux.
How do I download OpenVSCode Server?
Download a release of OpenVSCode Server from the
GitHub release area
. The releases are in sync with VS Code and change frequently. Make sure to download the arm64 version.
For example, use wget to download.
wget https://github.com/gitpod-io/openvscode-server/releases/download/openvscode-server-v1.101.2/openvscode-server-v1.101.2-linux-arm64.tar.gz
How do I install OpenVSCode Server?
Install the download by extracting the file
tar xvfz openvscode-server-v1.101.2-linux-arm64.tar.gz
How do I start OpenVSCode Server?
To start OpenVSCode Server run:
./openvscode-server-v1.101.2-linux-arm64/bin/openvscode-server
The server will print a URL to access VS Code in a browser. The URL is localhost URL. If your machine is a remote system or a Linux subsystem there are two options to connect using your local browser.
- Use SSH to forward port 3000 and connect using localhost
- Open port 3000 on the remote machine and use the public IP address instead of localhost
How do I connect using SSH port forwarding?
Refer to SSH for more info about SSH.
Use the -L option of ssh to forward port 3000.
ssh -L 3000:localhost:3000 user@ip-address
After connecting with port forwarding, use the localhost link printed by openvscode-server. It includes a token for security and will be similar to:
http://localhost:3000/?tkn=40711257-5e5d-4906-b88f-fe13b1f317b7
Open the link in your local browser and VS Code will appear.
How do I connect by opening a port on the remote machine?
The second option is to open port 3000 for access. On a cloud instance this involves changing the security group to open TCP port 3000. For best security, Make sure to open the port for your IP address only, not from all IP addresses.
Each cloud provider will have instructions on how to work with security group. Refer to the AWS documentation as an example.
With the port open, substitute the public IP address of the instance instead of localhost.
On ChromeOS you can use the Linux configuration settings to automatically do port forwarding. No SSH connection is needed.
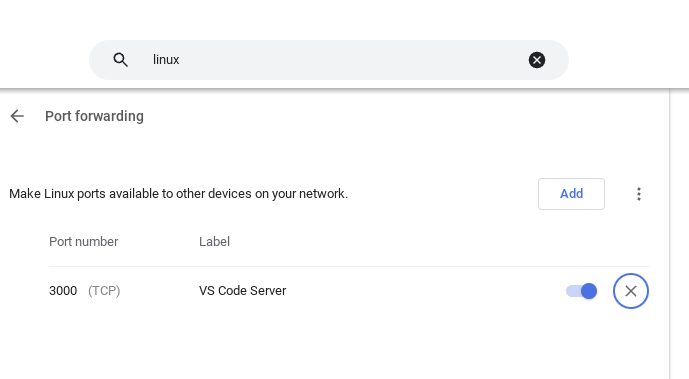
What other configuration options are available?
There are command line options to change the port, the token, and other configuration options. To see the options run:
./openvscode-server-v1.101.2-linux-arm64/bin/openvscode-server --help
If you are running all on a local machine the token can be eliminated using the --without-connection-token option.
It’s also possible to run an existing docker image which uses Ubuntu Linux for Arm and mounts your host directory to access files on your computer. Refer to the GitHub README for more information.
Install your favorite Extensions, select your favorite Color Theme, and enjoy VS Code in the browser.
Give Feedback
How would you rate this tool quick-install guide?
What is the primary reason for your feedback ?
Thank you! We're grateful for your feedback.
- Have more feedback? Log an issue on GitHub.
- Want to collaborate? Join our Discord server.