GitHub Copilot
About this Install Guide
| Reading time: | 10 min |
| Last updated: | 16 Dec 2025 |
| Reading time: |
| 10 min |
| Last updated: |
| 16 Dec 2025 |
| Author: | Pareena Verma, Arm
|
| Official docs: | View |
| Tags: |
| Author: |
| Official docs: |
| View |
| Tags: |
This guide shows you how to install and use the tool with the most common configuration. For advanced options and complete reference information, see the official documentation. Some install guides also include optional next steps to help you explore related workflows or integrations.
Overview
GitHub Copilot is an AI coding assistant that helps you write code faster and with less effort. It suggests whole lines or entire functions based on your comments and code context.
Copilot works seamlessly on Arm-based systems, including Linux distributions running on Arm servers, macOS on Apple Silicon, and Windows on Arm devices. This guide shows you how to install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code and extend it with the Arm MCP Server for Arm-specific development assistance.
For installation instructions for other editors (JetBrains IDEs, Neovim, Vim), see the GitHub Copilot documentation .
Before you begin
To use GitHub Copilot on Arm systems, you need a GitHub account with an active GitHub Copilot subscription.
If you don’t have a GitHub account, sign up on the GitHub website .
GitHub Copilot offers several subscription plans:
- Individual: for personal development
- Business: for teams and organizations
- Enterprise: for large-scale deployments
- Free tier: for verified students, teachers, and maintainers of popular open source projects
Select your GitHub Copilot subscription plan to get started.
After subscribing, verify your subscription is active by signing in to your GitHub account, navigating to Settings → Copilot, and confirming your subscription status shows as Active.
Install Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code runs natively on Arm systems and provides the best experience for GitHub Copilot.
Download Visual Studio Code from the Visual Studio Code download page and select the version for your operating system:
- For macOS (Apple Silicon): download the Apple Silicon version
- For Linux (Arm): download the Arm64
.debor.rpmpackage - For Windows on Arm: download the Arm64 installer
After downloading, run the installer and follow the installation prompts.
For Linux systems, install VS Code using your package manager. On Ubuntu and Debian-based distributions:
curl -L "https://code.visualstudio.com/sha/download?build=stable&os=linux-deb-arm64" -o vscode-arm64.deb
sudo dpkg -i vscode-arm64.deb
sudo apt-get install -f
Verify the installation
Open a terminal and verify the installation:
code --version
The output is similar to:
1.95.3
f1a4fb101478ce6ec82fe9627c43efbf9e98c813
arm64
Install GitHub Copilot extensions
Install the main extension
Open Visual Studio Code and install the GitHub Copilot extension:
- Open the Extensions view by selecting the Extensions icon in the Activity Bar or press
Ctrl+Shift+X(Windows/Linux) orCmd+Shift+X(macOS). - Search for GitHub Copilot.
- Select Install on the GitHub Copilot extension by GitHub.
Alternatively, install from the command line:
code --install-extension GitHub.copilot
Install Copilot Chat
For conversational AI assistance, install the GitHub Copilot Chat extension:
code --install-extension GitHub.copilot-chat
You can also search for GitHub Copilot Chat in the Extensions view and select Install.
Authorize GitHub Copilot
After installing the extensions, authorize GitHub Copilot:
- In VS Code, select the GitHub Copilot icon in the status bar (bottom right)
- Select Sign in to GitHub
- Follow the prompts to authorize the extension in your browser
- Return to VS Code to complete the setup
Verify Copilot is working
Test that GitHub Copilot is generating suggestions:
Create a new file by selecting File > New File or press Ctrl+N (Windows/Linux) or Cmd+N (macOS).
Save the file with a programming language extension (for example, test.py for Python, test.js for JavaScript, or test.go for Go).
Type a comment describing a function:
# Function to calculate fibonacci numbers
Press Enter to start a new line. Copilot analyzes your comment and suggests code as gray text in the editor.
Press Tab to accept the suggestion or Esc to dismiss it. Continue typing to see more suggestions as you work.
If you don’t see suggestions:
- Verify you’re working in the VS Code editor window (not a terminal)
- Check that the GitHub Copilot icon in the status bar shows it’s active
- Confirm you’re signed in to your GitHub account
- Verify your subscription is active
Work with GitHub Copilot modes
GitHub Copilot Chat in Visual Studio Code offers three modes; Agent, Edit, and Ask. Each mode helps you work with code in different ways.
Agent Mode
Agent Mode enables Copilot to take autonomous actions in your workspace. Copilot can read and analyze multiple files, make changes across your project, and create new files.
To use Agent Mode:
- Open the Copilot Chat panel by selecting the chat icon in the Activity Bar or press
Ctrl+Enter(Windows/Linux) orCmd+Ctrl+I(macOS) - Type
@workspacefollowed by your request
Example prompts:
Create a Python application to calculate fibonacci numbers@workspace add error handling throughout the application
Edit Mode
Edit Mode helps you modify code in your current file. Use this mode when you want to change existing code without creating new files. To use Edit Mode with selected code:
- Select the code you want to modify in your editor
- Press
Ctrl+I(Windows/Linux) orCmd+I(macOS) to open inline chat - Describe the changes you want
- Copilot shows a preview before applying changes
Example prompts:
- Select a function and ask:
Add input validation and error handling - Select a code block and ask:
Optimize this code for Arm architecture
Ask Mode
Ask Mode helps you understand code and learn concepts without making changes to your files.
To use Ask Mode:
- Open the Copilot Chat panel
- Type your question directly without any special prefixes
Example prompts:
How does this function work?(with code selected)What are the best practices for error handling in Python?Explain the difference between Arm64 and x86 architectures
Extend with the Arm MCP Server
Model Context Protocol (MCP) Servers extend GitHub Copilot’s capabilities by providing specialized tools and knowledge bases. The Arm MCP Server provides AI assistants with tools and knowledge for Arm architecture development, migration, and optimization.
About the Arm MCP Server
The Arm MCP Server includes several tools for Arm development:
- migrate-ease scan: analyzes codebases for x86-specific code that needs updating for Arm compatibility
- skopeo: inspects container images to check for ARM64 architecture support
- knowledge_base_search: searches Arm documentation and learning resources
- mca (Machine Code Analyzer): analyzes assembly code for performance on Arm architectures
- check_image: verifies Docker image architecture compatibility
Install the Arm MCP Server
You need Docker running on your system to use the Arm MCP Server. See the Docker install guide for instructions.
You can configure the MCP server using one of these methods:
Method 1: Install from GitHub MCP Registry (recommended)
The easiest way to install the Arm MCP Server is through the GitHub MCP Registry:
- Visit the Arm MCP Server registry page
- Select the Install MCP Server button
- From the dropdown, choose Install in VSCode
- VS Code opens with the Arm MCP Server installation page
- Select Install like you would with other extensions
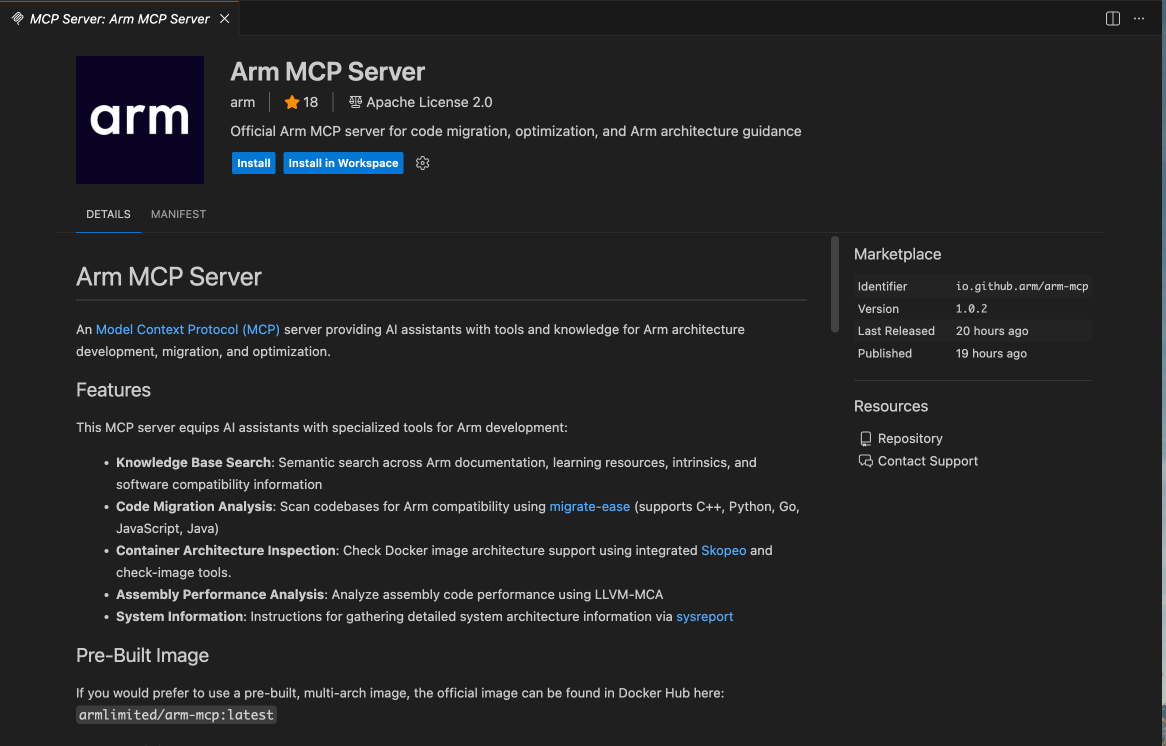 Install Arm MCP Server
Install Arm MCP Server
This method automatically installs the Arm MCP Server and pulls the Docker image. No manual configuration is required.
Method 2: configure manually
You can also configure the Arm MCP Server manually for more control over the installation.
First, ensure Docker is running on your system. Pull the Arm MCP Server image:
docker pull armlimited/arm-mcp:latest
Create a .vscode directory in your project root if it doesn’t exist, then create an mcp.json file:
mkdir -p .vscode
Create an mcp.json file in the .vscode directory with the following configuration:
{
"servers": {
"arm-mcp": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"--rm",
"-i",
"-v", "/path/to/your/codebase:/workspace",
"armlimited/arm-mcp:latest"
]
}
}
}
Method 3: user configuration (available in all workspaces)
Open the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows/Linux or Cmd+Shift+P on macOS) and select MCP: Open User Configuration. This opens your user-level mcp.json file located at ~/Library/Application Support/Code/User/mcp.json (macOS) or %APPDATA%\Code\User\mcp.json (Windows).
Add the following configuration to the user-level mcp.json file:
{
"servers": {
"arm-mcp": {
"type": "stdio",
"command": "docker",
"args": [
"run",
"--rm",
"-i",
"-v", "/path/to/your/codebase:/workspace",
"armlimited/arm-mcp:latest"
]
}
}
}
After saving your mcp.json file, a Start button appears at the top of the servers list. Select this button to start the Arm MCP Server.
How do I analyze a local codebase with the Arm MCP Server?
To analyze code in your workspace, mount your local directory to the MCP server’s /workspace folder using a volume mount.
Update your .vscode/mcp.json configuration to include the volume mount. Replace /path/to/your/codebase with the actual path to your project
For example, if your project is at /Users/username/myproject, the volume mount configuration is:
"-v",
"/Users/username/myproject:/workspace",
The volume mount (-v flag) connects your local directory to the MCP server’s /workspace folder. This enables the server to analyze code in your workspace. Use absolute paths for the source directory to avoid mounting errors.
After saving the .vscode/mcp.json file, select the Start button that appears at the top of the servers list to start the MCP server.
Verify the installation
After starting the MCP server, confirm it’s running:
- Open the Command Palette (
Ctrl+Shift+Pon Windows/Linux orCmd+Shift+Pon macOS) - Type and select MCP: List Servers
- Verify
arm-mcpappears as a Running configured server
Open the GitHub Copilot Chat panel by selecting the chat icon in the Activity Bar. In the chat box, select Agent from the mode dropdown.
To view available MCP tools, select the tools icon in the top left corner of the chat box. This opens the MCP server list showing all available tools from the Arm MCP Server:
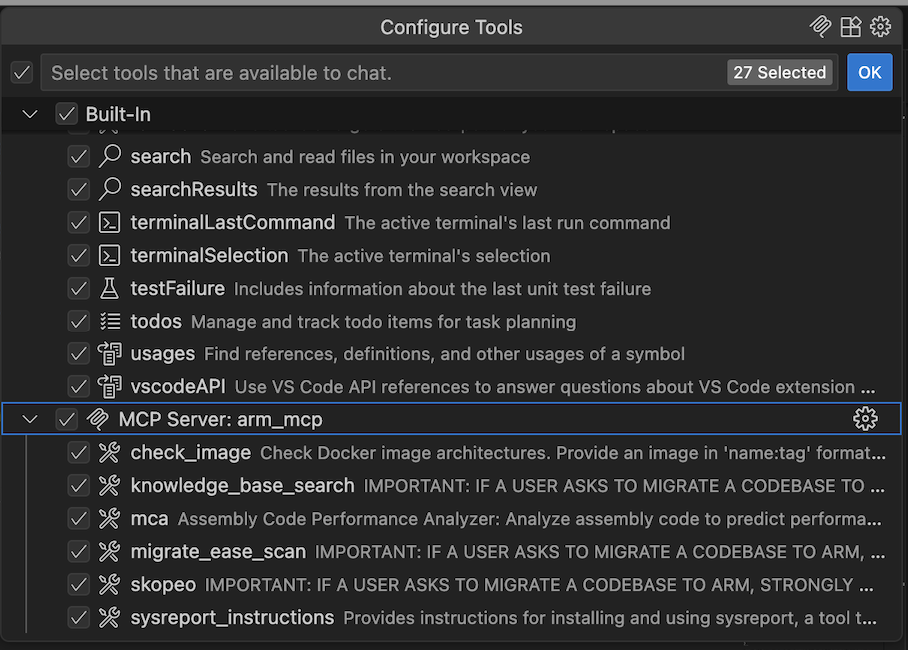 Tools from the Arm MCP Server
Tools from the Arm MCP Server
Use the Arm MCP Server
Ask Copilot to use specific Arm MCP tools in your prompts:
Use the Arm MCP Server to scan my codebase for x86-specific code
or
Check if the nginx:latest Docker image supports Arm64
Example prompts that use the Arm MCP Server:
Scan my workspace for code that needs updating for Arm compatibilityCheck if the postgres:latest container image supports Arm64 architectureSearch the Arm knowledge base for NEON intrinsics examplesFind learning resources about migrating from x86 to Arm
Troubleshooting MCP Server connections
This section helps you resolve common issues when installing and using GitHub Copilot with the Arm MCP Server on Arm systems. If you encounter problems not covered here, contact mcpserver@arm.com for support.
If the Arm MCP Server doesn’t connect:
- Verify Docker is running:
docker ps - Check that the image was pulled successfully:
docker images | grep arm-mcp - Review the VS Code Output panel (View → Output → GitHub Copilot Chat) for error messages
- Restart VS Code after making configuration changes
You’re now ready to use GitHub Copilot with the Arm MCP Server to enhance your Arm development workflow!
Give Feedback
How would you rate this tool quick-install guide?
What is the primary reason for your feedback ?
Thank you! We're grateful for your feedback.
- Have more feedback? Log an issue on GitHub.
- Want to collaborate? Join our Discord server.